NCERT Solutions Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 4 Introduction to Problem Solving
At Orchids International School, we believe it is essential to keep our young learners equipped with every resource. Class 11 Chapter 4 Computer Science deals with Problem Solving and Number Systems, an important part of Computing, due to just one, simple reason: this one deals with how data is represented and manipulated. This will explain several schemes of encoding and their applications, all of which would be integrated into the curriculum customized to hone problem-solving ability. Our Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 4 PDF elaborates to be of help in your learning through explanatory details on difficult concepts. Problem solving is the next chapter, which enables a person to develop skills in the analysis and assessment of theoretical knowledge on practical application. At Orchids International School, we ensure that children are provided with the right material and support in order to create a good base in the arena of computer science.
Download PDF For NCERT Solutions for Computer-Science Introduction to Problem Solving
The NCERT Solutions Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 4 Introduction to Problem Solving are tailored to help the students master the concepts that are key to success in their classrooms. The solutions given in the PDF are developed by experts and correlate with the CBSE syllabus of 2023-2024. These solutions provide thorough explanations with a step-by-step approach to solving problems. Students can easily get a hold of the subject and learn the basics with a deeper understanding. Additionally, they can practice better, be confident, and perform well in their examinations with the support of this PDF.
Download PDF
Access Answers to NCERT Solutions Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 4 Introduction to Problem Solving
Students can access the NCERT Solutions Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 4 Introduction to Problem Solving. Curated by experts according to the CBSE syllabus for 2023–2024, these step-by-step solutions make Computer-Science much easier to understand and learn for the students. These solutions can be used in practice by students to attain skills in solving problems, reinforce important learning objectives, and be well-prepared for tests.
Introduction to Problem Solving
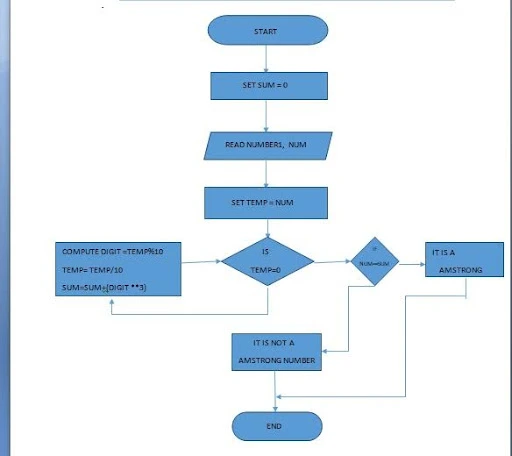
Draw a flowchart to check whether a given number is an Armstrong number. An Armstrong number of three digits is an integer such that the sum of the cubes of its digits is equal to the number itself. For example, 371 is an Armstrong number since 3**3 + 7**3 + 1**3 = 371.
Write pseudocode that reads two numbers and divide one by another and display the quotient.
number1 = float(input("Enter the first number: "))
number2 = float(input("Enter the second number: "))
if number2 == 0:
print("Error: Division by zero is not allowed.")
else:
quotient = number1 / number2
print("The quotient is:", quotient)
Write the pseudocode to print all multiples of 5 between 10 and 25 (including both 10 and 25).
# Define the start and end values
start = 10
end = 25
for number in range(start, end + 1):
# Check if the number is a multiple of 5
if number % 5 == 0:
# Print the number
print(number)
Give an example of a loop that is to be executed a certain number of times.
Suppose we have a certain number starting from 11 to 16. The loop will be executed as follow:
seti: = 11
fori: = 11 to 16 do
print i
end loop
Write an algorithm that accepts four numbers as input and find the largest and smallest of them.
Input first number
Input second number
Input third number
Input fourth number
Set lst = [ first , second, third , fourth ]
Sort the lst
lst.sort( )
Print greatest number is lst [ -1 ]
Print smallest number is lst [ 0 ]
What are conditionals? When they are required in a program?
In programming conditionals are used for providing the condition to values, input and output. There are various conditional statements are there to evaluate the expression. Generally conditional statement give us a output in the form of true or false which is known as Boolean value.
Conditionals are required in program to check whether the value is satisfied with required output or not.
Two friends decide who gets the last slice of a cake by flipping a coin five times. The first person to win three flips wins the cake. An input of 1 means player 1 wins a flip, and a 2 means player 2 wins a flip. Design an algorithm to determine who takes the cake?
def determine_winner(flips):
player1_score = 0
player2_score = 0
# Process each flip
for flip in flips:
if flip == 1:
player1_score += 1
elif flip == 2:
player2_score += 1
# Check if any player has won 3 flips
if player1_score == 3:
return "Player 1 wins the cake!"
elif player2_score == 3:
return "Player 2 wins the cake!"
return "No player won after 5 flips." #for tie conditions
result = determine_winner(flips)
print(result)
Suppose you are collecting money for something. You need ` 200 in all. You ask your parents, uncles and aunts as well as grandparents. Different people may give either ` 10, ` 20 or even ` 50. You will collect till the total becomes 200. Write the algorithm.
Step 1: Initialize total amount collected
total_amount = 0
Step 2: Continue collecting money until the total amount is at least 200
while total_amount < 200:
Step 3: Ask the contributor for their donation
donation = int(input("Enter the amount donated (10, 20, or 50): "))
Step 4: Check if the donation is valid
if donation in [10, 20, 50]:
Step 5: Add the donation to the total amount
total_amount += donation
Step 6: Print the current total amount
print("Current total amount collected:", total_amount)
Else:
Step 7: Inform the user about the invalid donation amount
print("Invalid donation amount. Please enter 10, 20, or 50.")
8: Final message when the total amount reaches or exceeds 200
print("Total amount of 200 has been reached.")
Write the pseudocode to print the bill depending upon the price and quantity of an item. Also print Bill GST, which is the bill after adding 5% of tax in the total bill.
Step 1: Input the price of the item
PRINT "Enter the price of the item: "
price = READ input
Step 2: Input the quantity of the item
PRINT "Enter the quantity of the item: "
quantity = READ input
Step 3: Calculate the total bill before tax
total_bill = price * quantity
Step 4: Calculate GST (5% of the total bill)
gst = total_bill * 0.05
Step 5: Calculate the total bill including GST
total_bill_with_gst = total_bill + gst
Step 6: Print the total bill before tax
PRINT "Total bill before GST: ", total_bill
Step 7: Print the GST amount
PRINT "GST (5%): ", gst
Step 8: Print the total bill including GST
PRINT "Total bill including GST: ", total_bill_with_gst
Write a pseudocode that will perform the following: a) Read the marks of three subjects: Computer Science, Mathematics and Physics, out of 100 b) Calculate the aggregate marks c) Calculate the percentage of marks.
Step 1: Read the marks for each subject
PRINT "Enter the marks for Computer Science (out of 100): "
computer_science_marks = READ input
PRINT "Enter the marks for Mathematics (out of 100): "
mathematics_marks = READ input
PRINT "Enter the marks for Physics (out of 100): "
physics_marks = READ input
Step 2: Calculate the aggregate marks
aggregate_marks = computer_science_marks + mathematics_marks + physics_marks
Step 3: Calculate the percentage of marks
// Total maximum marks for three subjects
total_maximum_marks = 300
// Percentage calculation
percentage = (aggregate_marks / total_maximum_marks) * 100
Step 4: Print the results
PRINT "Aggregate marks: ", aggregate_marks
PRINT "Percentage: ", percentage
Write an algorithm to find the greatest among two different numbers entered by the user.
Step 1: Read the first number
PRINT "Enter the first number: "
number1 = READ input
Step 2: Read the second number
PRINT "Enter the second number: "
number2 = READ input
Step 3: Compare the two numbers
IF number1 > number2 THEN
Step 4: Print the first number as the greatest
PRINT "The greatest number is: ", number1
ELSE
Step 5: Print the second number as the greatest
PRINT "The greatest number is: ", number2
END IF
Write an algorithm that performs the following: Ask a user to enter a number. If the number is between 5 and 15, write the word GREEN. If the number is between 15 and 25, write the word BLUE. if the number is between 25 and 35, write the word ORANGE. If it is any other number, write that ALL COLOURS ARE BEAUTIFUL.
Step 1: INPUT n
Step 2: IF n>5 And n<15 THEN
Step 3: PRINT “GREEN”
Step 4: ELSE IF n>15 And n<225 THEN
Step 5: PRINT “BLUE”
Step 6: ELSE IF n>25 And n<35 THEN
Step 7: PRINT “ORANGE”
Step 8: ELSE
PRINT “ALL COLOURS ARE BEAUTIFUL”
Step 9: End IF
Match the pairs
Write an algorithm to display the total water bill charges of the month depending upon the number of units consumed by the customer as per the following criteria:
-
for the first 100 units @ 5 per unit
-
for next 150 units @ 10 per unit
-
more than 250 units @ 20 per unit Also add meter charges of 75 per month to calculate the total water bill .
Step 1: INPUT units
Setp 2: SET bill := 0
Step 3: IF units > 250 THEN
COMPUTE bill := units * 20
ELSE
IF units <= 100 THEN
COMPUTE bill := units * 5
ELSE
COMPUTE bill := 100 * 5 + (units – 100) * 10
END IF
Step 4: END IF
Step 5: COMPUTE total_Bill := bill + 75
Step 6: PRINT total_Bil
Write a pseudocode to calculate the factorial of a number (Hint: Factorial of 5, written as 5!=5*4*3*2*1 )
INPUT number
SET factorial := 1, i := 1
WHILE i<= number DO
COMPUTE factorial := factorial * i
INCREASE i by 1
END LOOP
PRINT factorial
Following is an algorithm for going to school or college. Can you suggest improvements in this to include other options?
Reach_School_Algorithm
a) Wake up
b) Get ready
c) Take lunch box
d) Take bus
e) Get off the bus
f) Reach school or college
-
Wake up
-
Brush our teeth
-
Do some exercise
-
Take a bath
-
Get ready
-
Take a breakfast
-
Take a lunch box
-
Go to bus stand
-
Take a bus
-
Get off the bus
-
Reach school or college
Following is an algorithm to classify numbers as “Single Digit”, “Double Digit” or “Big”. Classify_Numbers_Algo
INPUT Number
IF Number < 9
“Single Digit”
Else If Number < 99
“Double Digit”
Else
“Big”
Verify for (5, 9, 47, 99, 100 200) and correct the algorithm if required.
For given data,
5 and 9 are single digit number, so it will print “single digit”
47 and 99 are double digit number, so it will print “double digit”
100 and 200 is a three digit number, so it will print “big”
Correct algorithm:
Step 1: INPUT Number
Step 2: IF Number <= 9
“Single Digit”
Step 3: Else If Number <= 99
“Double Digit”
Step 4: Else
“Big”
Step 5: End IF
For some calculations, we want an algorithm that accepts only positive integers upto 100.Accept_1to100_Algo
INPUT Number
IF (0<= Number) AND (Number <= 100)
ACCEPT
Else
REJECT
a) On what values will this algorithm fail?
b) Can you improve the algorithm?
a) On what values will this algorithm fail?
This algorithm fails at value 0. Because in condition we specify “greater than equal to operator”. So it will accept zero also.
b) Can you improve the algorithm?
Correct algorithm:
INPUT Number
IF (0<Number) AND (Number <= 100)
ACCEPT
Else
REJECT
Admissions Open for 2025-26

