Water for Class 6
Water is among the critical resources on the planet. It covers roughly 71% of the Earth's surface area and is very important for all life forms. Without water, no life can survive. We all need water for drinking, cooking, cleaning, farming, and industrial purposes. Plants and animals also need it in order to thrive. Water plays a crucial role in the interaction of different ecosystems and also stabilizes the temperature on the planet.
Why is Water Important?
Water is important because:
-
It is essential for drinking and to keep our bodies hydrated. Human beings can only last for a few days without water.
-
Plants require water for photosynthesis (to create food and oxygen), which is needed for their growth.
-
It maintains the Earth’s temperature by absorbing heat and regulating climate patterns.
-
Moreover, Industries and Agriculture use water to produce goods and grow crops.
-
It serves as a habitat for numerous fish and aquatic life that is essential for the food chain and ecosystem.
Sources of Water
There are sources of water. These include:
Surface water – Water that collects on the surface, such as rivers, lakes, and ponds. These are the typical sources of fresh water.
Groundwater – Water that exists below the surface of the Earth in underground facilities and wells.
Rainwater – Water that falls into the ground out of clouds as rain, which can additionally be harvested.
Glaciers – These are large frozen bodies of water that hold fresh water for long periods.
|
Source |
Description |
|
Surface Water |
Found in rivers, lakes, and oceans and is used for drinking and irrigation. |
|
Groundwater |
Found under the Earth’s surface, usually extracted through wells and boreholes. |
|
Rainwater |
Collected from rainfall, often used in rainwater harvesting. |
|
Glaciers |
Frozen fresh water in mountains and poles acts as long-term water reserves. |
Did You Know: Approximately 3 percent of the water on Earth is freshwater, and most of it is frozen in glaciers.
Physical States of Water
Water can be found in three physical states:
-
Solid: Ice, glaciers, and snow – It is formed when the temperature falls below freezing.
-
Liquid: The most familiar state of water used for drinking, cooking, and cleaning.
-
Gas: Water vapour in the air (as clouds and humidity)
Fun Fact: Water expands when frozen, which is why ice floats.
Water Cycle
The water cycle (Hydrological Cycle) is the ongoing process of water on, above, and below the Earth's surface. It has the following steps:
-
Evaporation: The evaporation of water from the oceans, rivers and lakes - when the water changes into water vapour through the heat of the sun.
-
Condensation: The water vapor cools, clouds form, and moisture builds up.
-
Precipitation: The water falls back to the earth as rain, snow, or hail that fills surface water bodies.
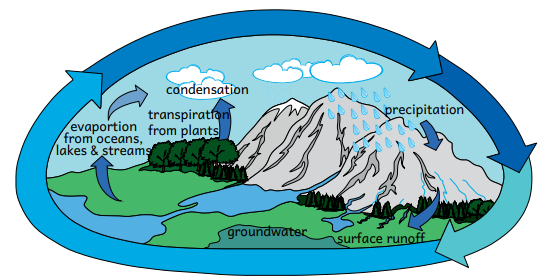
Water Cycle
|
Process |
Description |
|
Evaporation |
Water changes from liquid to gas due to heat. |
|
Condensation |
Gas changes to liquid and forms clouds. |
|
Precipitation |
Water falls as rain, snow, or hail, returning to the Earth's surface. |
Conservation of Water
Water conservation is the use and management of water resources and the waste of usage. Water, although renewable in some form, is a scarce resource, and it must be conserved for times to come.
Why is there a need for Water Conservation?
Here is why water conservation is essential:
- In some places, droughts cause water shortages and crops die.
- Some areas are water-stressed, leading to implications for human survival and health.
- Freshwater is becoming unsafe due to rising water pollution.
Fun Fact: A leaking tap can waste more than 3,000 liters of water in a year.
Different Methods of Water Conservation
Ways to save water include:
- Fixing leaks right away to conserve hundreds of gallons of water.
- Using water-saving appliances such as low-flow showers and dual-flush toilets.
- Harvesting rainwater to store water for use at home and in agriculture.
- Using recycled water for gardening and washing.
What is Rainwater Harvesting?
Rainwater harvesting means collecting and storing rainwater for future use. It promotes and encourages minimizing the use of known water sources, as well as alternative water purification sources, particularly in arid environments.
One such method is Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting (RRWH), which is the process of collecting rainwater that falls on the roof through pipes and storing it in tanks for further supply.
What is a Flood?
Flood Description: A flood is an overflow of water onto land that is normally dry. Flood is a natural disaster which occurs due to heavy rainfalls, river overflowing or dam breaking that causes extensive damage to the property of human beings and leads to loss of human lives.
Causes of Floods
- Excess rain that surpasses the soil's absorptive capacity, leading to water accumulation.
- Melting glaciers raise water levels in rivers and lakes.
- Few systems of drainage and poor design of drainage lead to the accumulation of water, affecting the flow.
Effects of Floods
- Losses to homes and property, causing financial damages.
- Death toll and crop loss impact the food chain.
- Widespread spread of water disease due to contaminated water.
Measures to Prevent Floods
- Building dams to manage the flow of water.
- Helping drainage systems so that water passes without any issue.
- Replanting trees to retain water and avoid soil erosion.
What is a Drought?
A drought is a prolonged period of low rainfall. Water shortages and crop failures are the results of drought.
10 Ways to Save Water:
- Switch off taps while cleaning your teeth to prevent unnecessary wastage.
- To avoid water loss, fix leaking taps and pipes.
- Install a water softener system to increase efficiency and reduce water wastage.
- Harvest rainwater for gardening, laundry, and even household use.
- Run washing machines using less water when washing clothes.
- Try to water plants in the morning or evening to minimize evaporation.
- Take shorter showers to save water.
- Use wastewater when possible, such as using dishwater for plants.
- If you wash your car, use a bucket, not a hose - and save the water.
- The more people you tell about the importance of water conservation, the more that they will be encouraged to do their bit and for others too.
Water is considered a scarce resource, and we need to use it for wisely so that it is available for future generations.
Things you have learned!
- Water covers 71% of Earth's surface and is the foundation of life.
- It has 3 different physical forms - solid, liquid, and gas.
- The water cycle is comprised of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
- Fresh water is a finite resource and must be conserved for it to be available in the future.
- Conserving methods such as repairing leaks, water-efficient appliances, rainwater harvesting, etc.
- Floods, droughts, and the impact on ecosystems and human life make water a critical utility.
- The importance of saving water can be taught to one and all as it will help save this natural resource for the next generations.

