Vegetative Propagation: Definition, Types, Examples
Vegetative propagation is an asexual method where new plants grow from roots, stems, or leaves without seeds.
Types of Vegetative Propagation
| Type | Description | Example |
| Natural Vegetative Propagation | Happens naturally through modified stems, roots, or leaves | Tubers (Potato), Runners (Strawberry) |
| Artificial Vegetative Propagation | Done by humans to produce identical plants | Grafting (Mango), Cutting (Rose) |
Natural Vegetative Propagation
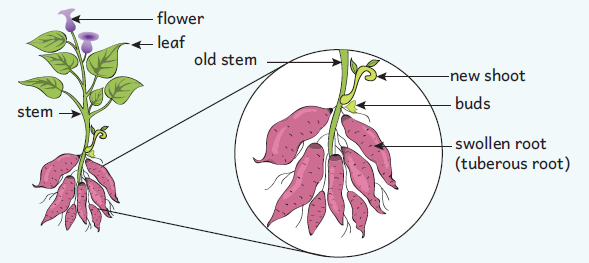
Tubers in Sweet Potato
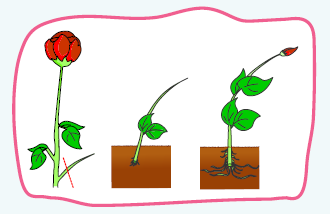
Cutting in Rose.
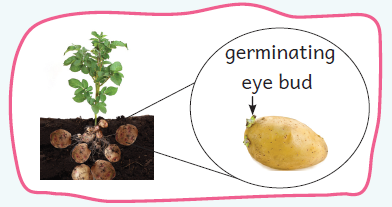
Eye Buds in Potato
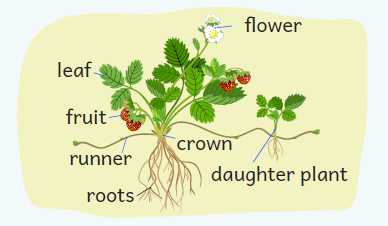
Runners in strawberry
Artificial Vegetative Propagation
-
Cuttings – A piece of stem or leaf is cut & placed in soil (e.g., Rose, Money plant).
-
Grafting – A branch from one plant is joined to another plant (e.g., Mango, Apple).
-
Layering – A stem is bent to the ground & covered with soil to form new roots (e.g., Jasmine, Strawberry).
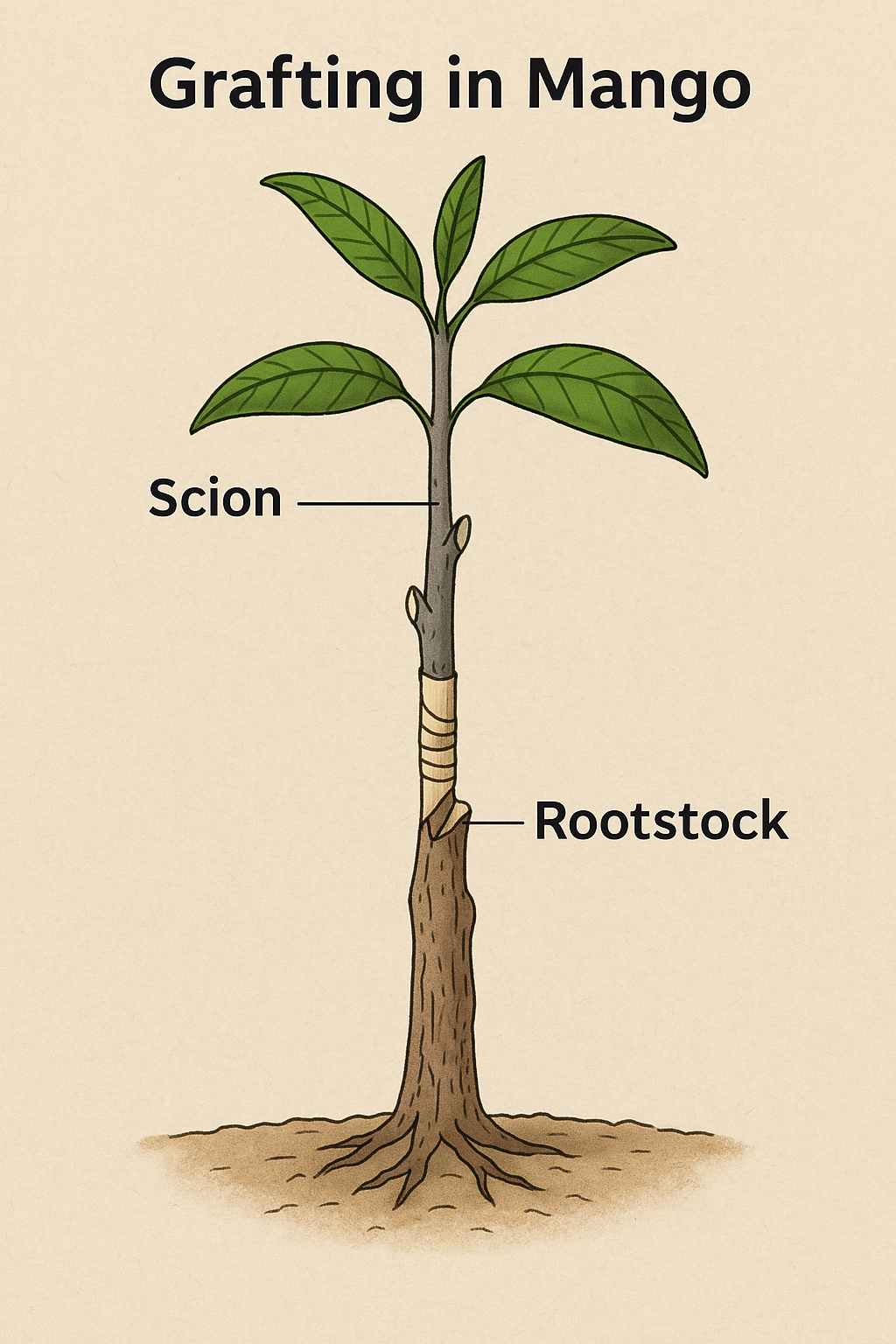
Grafting in Mango
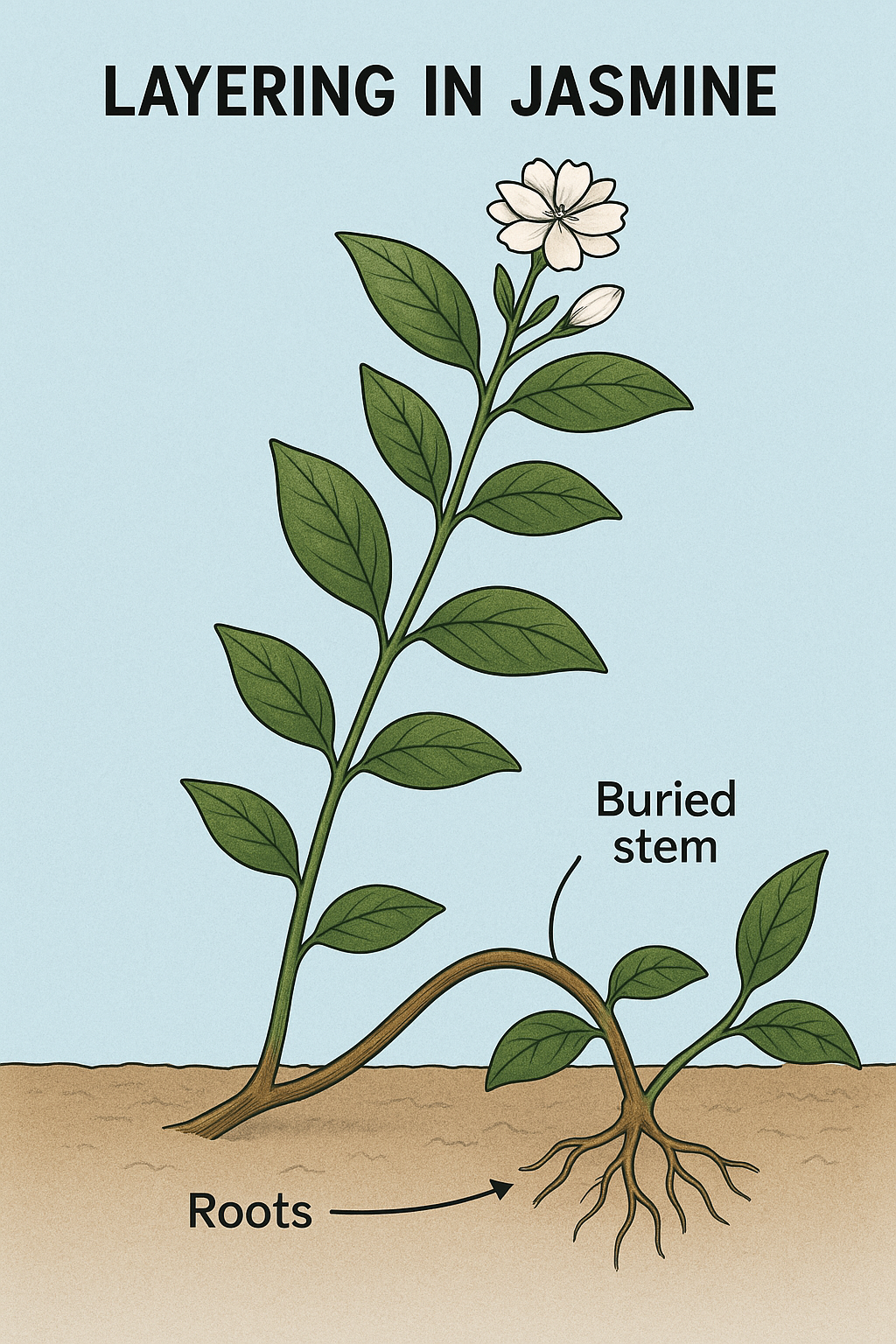
Layering in Jasmine
Cutting in Rose
Vegetative propagation through leaves and spores
-
The Bryophyllum is a plant whose leaves can grow into new plants. The leaves of the Bryophyllum are broad & fleshy. They have tiny buds (plantlets) present at their margins.
-
When the buds fall on moist soil, they germinate & grow into adult plants.
-
Leaves of Begonia also grow into new plants from its buds.

Plantlets in Bryophyllum

Vegetative Propagation in Begonia
Conclusion: Vegetative propagation is a way plants grow without using seeds. It can happen on its own (natural) or with our help (artificial). Plants like rose, potato, mango, and Bryophyllum are some examples of this way of reproduction.

