Sources of Food - Plants and Animals Products for Class 6
All life forms depend on food for their existence. All living things need food to survive: it gives us energy, aids growth, and supports keeping healthy. The first thing to consider about food is that it all comes from somewhere, plants & animals, in one way or another. Rice is extracted from plants, whereas milk is derived from animals. Knowing the origins of food is key to choosing better food and enjoying the biodiversity of life.
Food Ingredients
The food ingredients are the components utilized to create a dish. We will be able to answer questions about the different ingredients we want to put in each dish, where they are, and whether they are grown in plants or harvested from animals.
Examples of Food Ingredients
|
Food Item |
Ingredients |
Source of Ingredients |
|
Rice Porridge |
Rice, Water, Salt |
Plant, Natural |
|
Omelet |
Egg, Oil, Salt, Spices |
Animal, Plant |
|
Vegetable Curry |
Vegetables, Spices, Oil, Salt |
Plant |
|
Chicken Soup |
Chicken, Water, Spices |
Animal, Plant |
Sources of Food
There are two main sources of food:
Plant-Based Food
Plants provide a variety of food items, including:
-
Cereals: Cereals are seeds, mostly obtained from grasses cultivated for food grains. Cereals such as wheat, rice, barley, maize & oats are rich sources of carbohydrates. They provide energy to our body (Wheat, Rice, Maize)

-
Fruits & Vegetables: Plants provide us with different fruits & vegetables which are a rich source of vitamins & minerals. They keep our bodies healthy and fit. (Apple, Mango, Banana, Carrot, Spinach, Potato)

-
Spices: Turmeric, clove, cumin, chilli, cinnamon, mustard etc., are some of the commonly used spices in the preparation of food. They are used for flavouring, colouring & preserving food.

-
Pulses: Pulses are seeds from leguminous plants, where the seeds are found in pods. Green gram, black gram, peas, kidney beans and chickpeas are some of the common pulses we eat in our day-to-day lives. They are a rich source of proteins which help in our growth & repair of tissues in our body. (Lentils, Chickpeas)

-
Medicines: Basil, dandelion, garlic, parsley, etc., are some of the common medicinal plants that help us to improve our health.

-
Beverages: Tea & coffee are widely consumed beverages. Tea is prepared from dried tea leaves where as coffee is prepared from the dried seeds of coffee plants.

-
Oils: Oil is extracted from the seeds of some plants such as mustard, soybean, groundnut, sunflower, etc. It is used primarily for cooking. It provides warmth & energy to our body. (Mustard oil, Coconut oil)

Animal-Based Food
Animals provide food products such as:
-
Meat: Buffaloes, pigs, goats, hens, ducks, etc., give us meat. The flesh of animals is called meat.
-
Dairy Products: Milk contains essential nutrients like calcium, phosphorus, potassium, proteins, vitamin D, and vitamins B1, B2 & B12. Cows, buffaloes, goats, and camels are some of the milk-giving animals. Products such as cheese, paneer, curd, etc., made from milk are called dairy products. (Milk, Cheese, Butter)

-
Eggs: We obtain eggs from hens, quails, turkeys, and ducks. It is a rich source of protein, vitamins & fat.
-
Honey: Honeybees prepare honey from the nectar of flowers. Once the nectar is collected, it is mixed with the bee enzyme in the bee's stomach. Bee enzyme is secreted from the mouth of the bee, which helps in the conversion of nectar into honey. Then, it is stored in the beehive for future use. (Collected by bees from flowers)

"Ready to fuel your body? Let’s find out what’s in your food!"
Comparison of Plant and Animal-Based Food
|
Feature |
Plant-Based Food |
Animal-Based Food |
|
Example |
Fruits, Vegetables |
Meat, Eggs |
|
Nutrients |
Vitamins, Fiber |
Proteins, Fats |
|
Growth Source |
Grows in soil |
Comes from animals |
|
Example Dish |
Salad, Rice, Juice |
Chicken Curry, Boiled Egg |
Edible Parts of Plants
Different parts of plants are eaten as food.
|
Plant Part |
Examples |
|
Roots |
Carrot, Beetroot, Radish |
|
Stems |
Sugarcane, Ginger, Potato |
|
Leaves |
Spinach, Cabbage, Mint |
|
Flowers |
Cauliflower, Broccoli |
|
Fruits |
Apple, Mango, Tomato |
|
Seeds |
Wheat, Rice, Mustard |
Sprouting of Seeds
Sprouting is the process in which seeds germinate & produce tiny white shoots. It increases the nutritional value of the seeds.
Steps to Sprout Seeds at Home:
- Take some seeds (like mung beans or chickpeas).
- Soak them in water overnight.
- Drain the water & keep them in a moist cloth for a day.
- After 1-2 days, small white shoots will appear.

Nutritional Benefits of Sprouted Seeds
- Rich in vitamins & minerals.
- Easy to digest.
- Contains more protein than non-sprouted seeds.
"Mix & Match Time – Create a balanced meal with all food components!" Click here to know how!
Animals and Their Food Habits
Animals need food to survive, grow, and reproduce. Different animals have different food habits depending on their habitat, body structure, & digestive system. Based on their diet, animals are classified into various groups.
Types of Animals Based on Food Habits
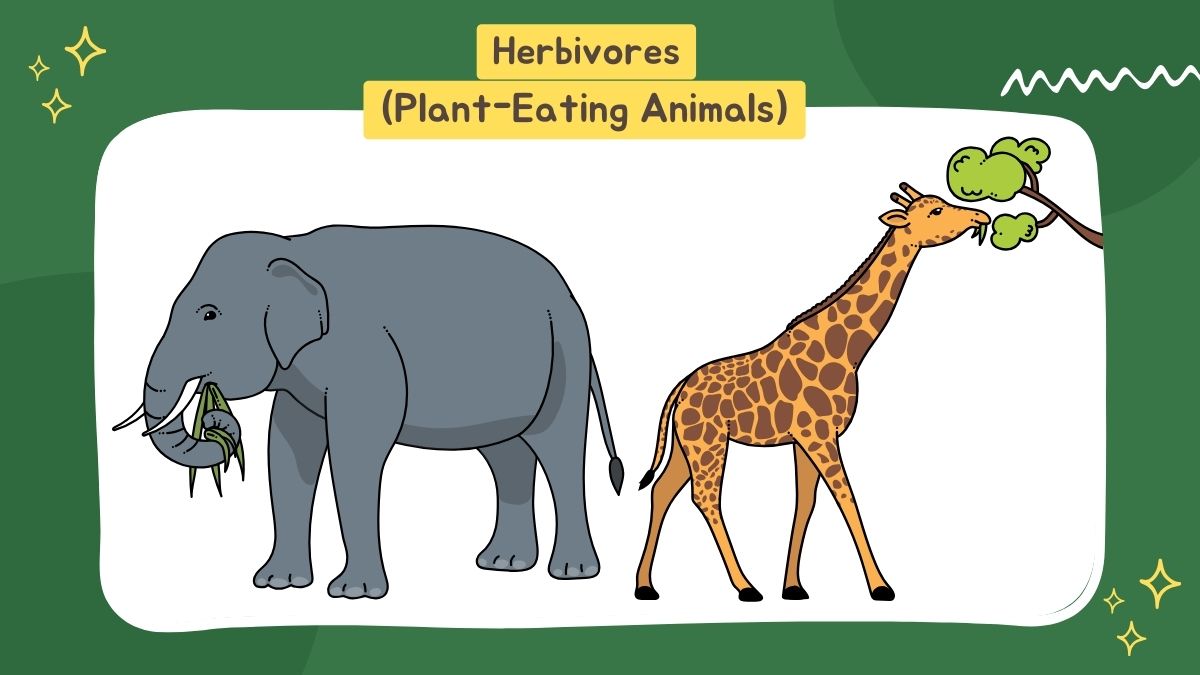
1. Herbivores (Plant-Eating Animals)
Herbivores are vegan creatures. Their flat, broad teeth allow them to chew and grind plant material effectively. Their digestive system is uniquely suited to digest tough plant fibers like cellulose. Certain herbivores — such as cows & deer — have multiple stomach chambers to help digest their food.
Main Features:
- Avoid eating anything other than plants, leaves, fruits, or vegetables.
- Teeth are shaped flat and broad for grinding food.
- The digestive tract long for digesting fibrous plant material.
- Some chew cud (ruminants), such as cows & goats.
2. Carnivores (Meat-Eating Animals)
Carnivores are animals that eat other animals. They have sharp teeth and powerful jaws for tearing flesh. Their digestive system is shorter compared to that of herbivores because meat is far easier to digest. Examples of carnivores are lion, tiger, eagle & snake. Some carnivores - e.g., snakes eat their prey whole.
Main Features:
- Eat the meat of other animals.
- Teeth are sharp for efficient meat tearing.
- Robust muscles of the jaw, aiding in killing & extracting prey.
- A short digestive tract to rapidly digest the flesh.

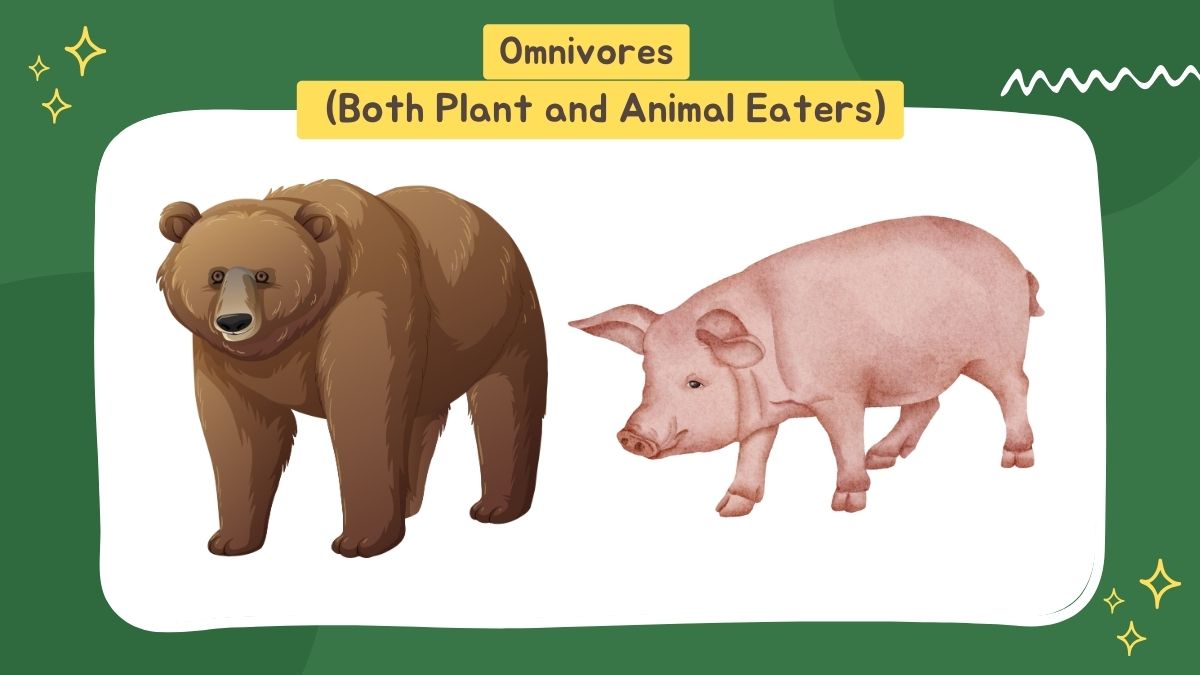
3. Omnivores (Both Plant and Animal Eaters)
This is because omnivores eat both animal and plant-based food. They also have a mix of sharp teeth (for shredding meat) and flat molars (for chewing plants).
Omnivores: We have omnivores like humans, bears, crows, pigs & others. These creatures have a versatile diet with a unique ability to adjust to varying food supplies.
Main Features:
- Consumes both plants & animals.
- Have sharp and flat teeth to tear & grind food.
- The digestive system evolved to handle multiple foods.
- Feed on so many different kinds of things that they can live in many different environments.
4. Scavengers (Animals That Eat Dead Organisms)
The dead animals are food for scavengers. They help clean the environment by recycling decaying matter, there by preventing it from accumulating. Such animals are known as scavengers, including vultures, hyenas, & crabs.
Main Features:
- Scavenge on the carcasses of dead & decaying animals.
- They are well adapted to tolerate bacteria and toxins in their food.
- Assist in maintaining ecological balance by cleaning up decaying matter.
- They have excellent vision and a keen sense of smell to find carcasses.
5. Decomposers (Microorganisms That Break Down Organic Matter)
These decomposers are organisms such as bacteria and fungi that decompose or turn decaying plants & animals into simpler substances. They are helping to recycle nutrients back into the soil.
Main Features:
- Decomposes dead & decaying organic matter.
- Break down complex organic matter into simple nutrients.
- They contribute to soil improvement & nutrient cycling necessary for the balance of ecosystems.
Fun Facts
- Rice serves as a staple food for more than half the world’s population.
- Chicken is the most widely chosen meat in the world.
- Banana is classified as berries, but strawberries aren’t real berries.
- They would, however, eat a lot of plants, which cows have four stomach compartments to aid in digestion.
Things You Have Learned!
- Understood that food comes from plants and animals.
- Recognized ingredients like rice from plants and milk from animals.
- Distinguished between plant-based foods (fruits, vegetables) and animal-based foods (meat, eggs).
- Identified the different parts of plants we eat, such as roots, stems, leaves, and fruits.
- Learned that animals have different food habits, like herbivores eating plants and carnivores eating meat.

