Forms of Matter: Properties of Solid, Liquid, and Gas
In the previous lesson, we discussed the concept of “Matter”. In this lesson, we shall discuss the “Forms of Matter”. But, before we proceed, let us quickly refresh your knowledge of “Matter”
-
Matter is anything that has ________ and takes up ________.
-
Matter is made up of tiny building blocks called ________.
-
The amount of matter in an object is its ________.
Answer to Q.No.1 - Mass, Space
Answer to Q No.2 - Atoms
Answer to Q No.3 - Mass
Forms of Matter / States of Matter
Matter is a substance that exists in different forms based on the arrangement and behavior of the respective particles. The three forms of Matter or the three states of Matter are Solid, Liquid, and Gas. These forms of matter are present everywhere around us. Let us learn how to view and identify them as Solid, Liquid, and Gas, and let us study each of them in detail:
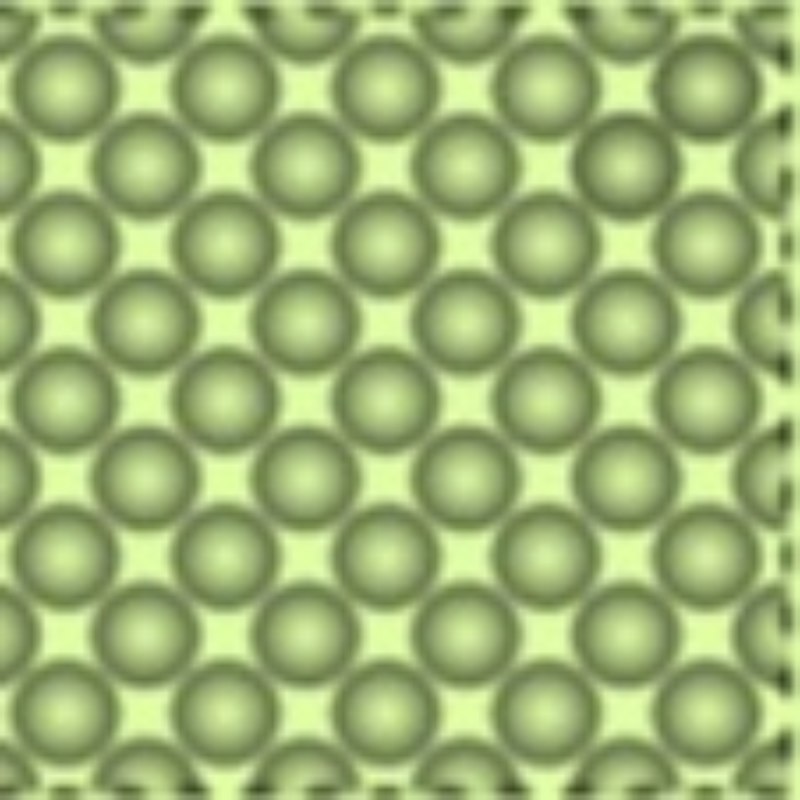
1. Solids
Just glance around and you may spot several objects having a definite shape and size. Touch them and you will realize that it has a proper form. Such objects are called Solids. The particles inside a Solid are tightly packed and do not move freely. The following are its properties -
-
Solids have a definite size, shape, mass, and volume.
-
A solid does not change its shape when it is moved.
-
The molecules of solids are tightly packed.
-
Molecules in solids do not move freely but are stuck in one place.
-
Sound travels fastest through solids.
-
It is the maximum attraction force between the molecules of solid materials.
Real-Life Examples of solids:
Stones, pebbles, wood, chalk, buildings, tables, chairs, pencils, books, diamonds, etc.
Test your Understanding
1. Which among the following is an example of a Solid state?
a) Mobile Phone
b) Water
c) Hydrogen
2. Which state of matter is “Pencil”?
a) Solid State
b) Liquid State
c) Gaseous State
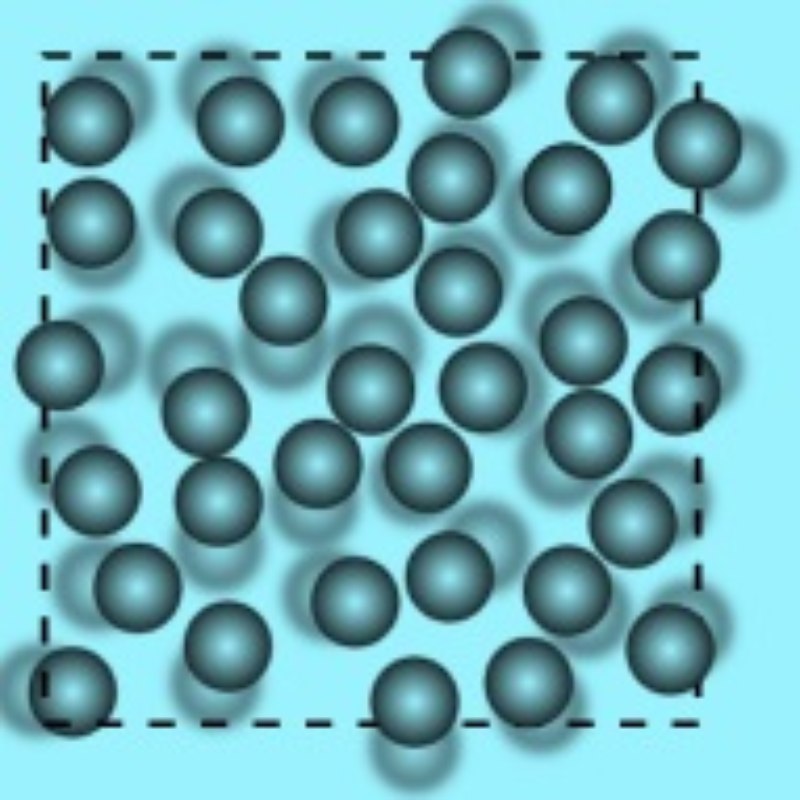
2. Liquids
When we feel thirsty, we drink water, right? Water flows freely but has a constant volume. It is less rigid than solids and takes the shape of the container it is poured in. It means it does not have a definite shape like a solid object. Such substances are called Liquids. The particles in a liquid are held together but less tightly packed than in a solid substance. The following are its properties:
-
Liquids do not have definite shapes and sizes.
-
Liquids have a definite volume.
-
They may take the shape of any containing vessel they are poured into.
-
The molecules of a liquid are loosely held together and move freely.
-
The molecules of the liquids are loosely packed, thus they can be able to take the shape of the container they are being poured into.
-
The force of attraction between the molecules of a liquid is moderate.
-
It can be measured in terms of volume.
-
The shape and size of a liquid cannot be measured.
-
A liquid moves from the higher level to the lower level.
Real-Life Examples of Liquids:
Oil, water, milk, blood, gasoline, coffee, tea, honey, maple syrup, etc.
Test your Understanding
1. Which among the following is an example of a Liquid state?
a) Car
b) Petrol
c) Carbon dioxide
2. Which state of matter is “Oil”?
a) Solid State
b) Liquid State
c) Gaseous State
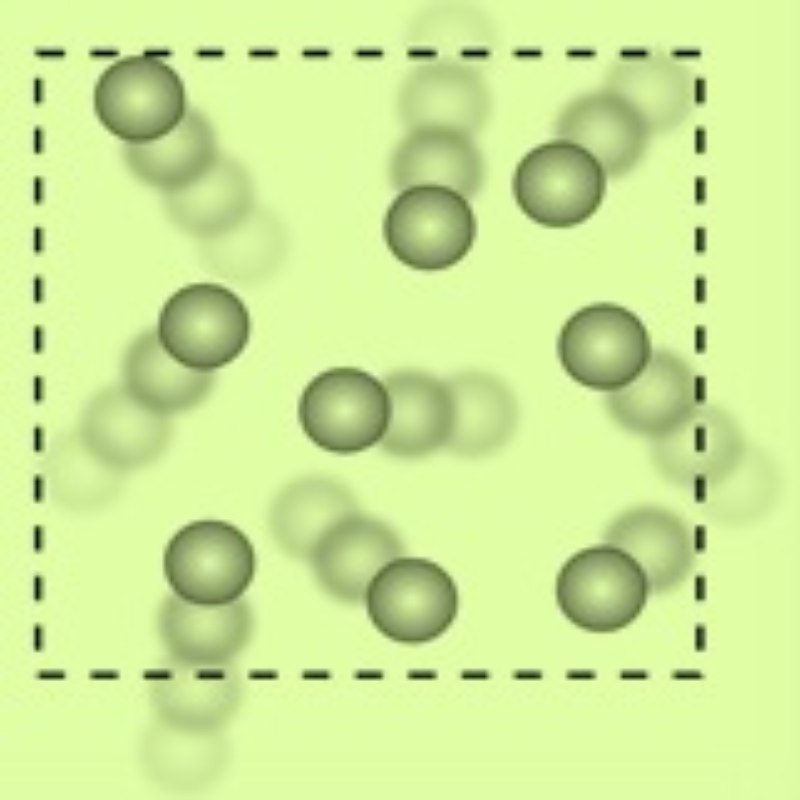
3. Gas
We breathe Air. To be more specific, we breathe in Oxygen. Just observe. Does it have a fixed shape or a volume? No. Such substances are called “Gas”. The particles in a Gas are widely spaced and move freely at a high speed. The properties of Gas are distinctly different from those of Solids and Liquids as listed below:
-
There are gases all over the world and they have occupied nearly all the vacuum regions
-
Balls, balloons, and bubbles are filled with gases.
-
So is the case with air
-
There is a lot of space between the molecules of gases and they can readily move.
-
Gas molecules move a little faster than their liquid counterparts.
-
Gases do not have any definite size, shape, or volume.
-
There are virtually no forces of attraction between most of the gas molecules.
-
It simply means nothing to hold its definite shape or volume.
Real-Life Examples of Gases
Gases mainly include oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen, helium, steam, etc. The steam from a cup of coffee, the fumes emitted from vehicles, and Factory fumes emitted from High-rise Chimneys are all examples of gases.
Test your Understanding
1. Which among the following is an example of a Gaseous state?
a) Tree
b) River
c) Oxygen
2. Which state of matter is “Nitrogen”?
a) Solid State
b) Liquid State
c) Gaseous State
What are the main differences between solid, liquid, and gas?
Solids have a definite shape and volume. Liquids have a definite volume but not a definite shape as they take the shape of a container. Gases have neither a definite shape nor volume and they fill up all the available space. All these states differ in their arrangement, motion, density, and forces between molecules.
What is the process of a Solid getting converted into Liquid called?
The process of a solid turning into a liquid form is called Melting. It normally occurs when the solid is exposed to heat and pressure. Common examples are the melting of ice into water, the melting of butter, chocolates, candle wax, etc.
What is the process of a Liquid getting converted into Gas called?
The process of a Liquid turning into Gas is called Evaporation or Vaporization. Even this occurs when the liquid gets heated and there is a temperature rise. Common examples are steam evaporating from boiling water, and a spray of a perfume that is filled with liquid but spreads its fragrance around in gaseous form.
Quiz
1. Which of the following states of matter has a definite shape and volume?
-
A) Solid
-
B) Liquid
-
C) Gas
-
D) Plasma
2. What happens to a liquid when it is heated?
-
A) It melts.
-
B) It solidifies.
-
C) It evaporates.
-
D) It sublimates.
3. Which of the following statements is true about gases?
-
A) Gases have a fixed volume but no fixed shape.
-
B) Gases have neither a fixed shape nor a fixed volume.
-
C) Gases have a fixed shape but no fixed volume.
-
D) Gases have both a fixed shape and a fixed volume.
4. Which of the following describes the particle arrangement in a solid?
-
A) Particles are loosely packed and move freely.
-
B) Particles are tightly packed in a fixed structure.
-
C) Particles move quickly and are far apart.
-
D) Particles are free to move past each other.

