NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 - Motion and Time
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13, "Motion and Time," are valuable study materials that can significantly aid students in preparing for the CBSE Class 7 examination. These meticulously crafted solutions for Chapter 13 of Class 7 Science, designed by expert teachers, align with the latest syllabus of the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE).
Access Answers to NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 - Motion and Time
Students can access the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 - Motion and Time. Curated by experts according to the CBSE syllabus for 2023–2024, these step-by-step solutions make Science much easier to understand and learn for the students. These solutions can be used in practice by students to attain skills in solving problems, reinforce important learning objectives, and be well-prepared for tests.
Motion and Time
Classify the following as motion along a straight line, circular or oscillatory motion:
(i) Motion of your hands while running.
(ii) Motion of a horse pulling a cart on a straight road.
(iii) Motion of a child in a merry-go-round.
(iv) Motion of a child on a see-saw.
(v) Motion of the hammer of an electric bell.
(vi) Motion of a train on a straight bridge.
i) Oscillatory
ii) Motion along a straight line
iii) Circular motion
iv) Oscillatory motion
v) Oscillatory motion
vi) Motion along a straight line.
Which of the following are not correct?
(i) The basic unit of time is second.
(ii) Every object moves with a constant speed.
(iii) Distances between two cities are measured in kilometres.
(iv) The time period of a given pendulum is constant.
(v) The speed of a train is expressed in m/h.
Incorrect statements are:
(ii) Every object moves with a constant speed.
(iv) The time period of a given pendulum is constant.
(v) The speed of a train is expressed in m/h.
A simple pendulum takes 32 s to complete 20 oscillations. What is the time period of the pendulum?
Number of oscillations = 20
Total time taken to complete 20 oscillations = 32 s
The distance between two stations is 240 km. A train takes 4 hours to cover this distance. Calculate the speed of the train.
Distance between two stations = 240 kms
Total time take = 4 hrs/240 minutes
= 60 km/h
The odometer of a car reads 57321.0 km when the clock shows the time 08:30 AM. What is the distance moved by the car, if at 08:50 AM, the odometer reading has changed to 57336.0 km? Calculate the speed of the car in km/min during this time. Express the speed in km/h also.
Initial reading of the odometer = 57321.0
Final reading of the odometer = 57336.0
Distance covered by the car = Final reading of the odometer – Initial reading of the odometer
= 57336.0 – 57321.0 = 15 kms
Starting time of car is 8:30 and it stops at 8:50
Hence, time taken by car = 20 mins
= 45 km/h
Salma takes 15 minutes from her house to reach her school on a bicycle. If the bicycle has a speed of 2 m/s, calculate the distance between her house and the school.
Time taken by Salma to reach her school by bicycle = 15 mins= 15 x 60 = 90 s
Speed of Salma’s bicycle= 2m/s
Distance covered = speed x time taken
= 2 x 900 = 1800 m
1000m = 1 km
= 1.8 kms
Show the shape of the distance-time graph for the motion in the following cases:
(i) A car moving with a constant speed.
(ii) A car parked on a side road.
Which of the following relations is correct?
(i) Speed = Distance × Time
(ii) Speed = Distance/Time
(iii) Speed = Time/Distance
(iv) Speed = 1/Distance x Time
(ii) Speed = Distance/Time
The basic unit of speed is:
(i) km/min
(ii) m/min
(iii) km/h
(iv) m/s
(iv) m/s
A car moves with a speed of 40 km/h for 15 minutes and then with a speed of 60 km/h for the next 15 minutes. The total distance covered by the car is:
(i) 100 km
(ii) 25 km
(iii) 15 km
(iv) 10 km
(ii) 25 km
Calculation:
When the speed of the car is 40 km/h
Time taken = 15 min = 15/60 = 0.25 h
Distance covered d1 = speed x time taken
= 40 x 0.25 = 10 kms
When the speed of the car is 60 km/ h
Distance covered d2 = speed x time taken
= 60 x 0.25= 15 kms
Total distance covered by the car = d1 + d2
= 10 + 15
= 25 kms
Fig. 13.15 shows the distance-time graph for the motion of two vehicles A and B. Which one of them is moving faster?
Vehicle A is moving faster than vehicle B.
Which of the following distance-time graphs shows a truck moving with speed which is not constant?
iii)
Suppose the two photographs, shown in Fig. 13.1 and Fig. 13.2, had been taken at an interval of 10 seconds. If a distance of 100 metres is shown by 1 cm in these photographs, calculate the speed of the fastest car.
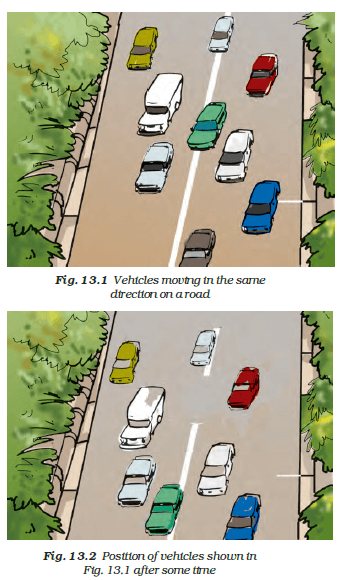
The distance covered by the blue car (as evident from the photograph) from one horizontal white strip to another, which is measured by scale is 1.2 cm.
It is given that 1 cm is equivalent to 100 m.
Therefore, 1.2 cm is equivalent to 120 m.
Distance travelled by the car = 120 m
Time taken to cover this distance = Time interval between the two photographs = 10 s
= 120/10
= 12 m/s
Frequently Asked Questions
The NCERT solution for Class 7 Chapter 13: Motion and Time is important as it provides a structured approach to learning, ensuring that students develop a strong understanding of foundational concepts early in their academic journey. By mastering these basics, students can build confidence and readiness for tackling more difficult concepts in their further education.
Yes, the NCERT solution for Class 7 Chapter 13: Motion and Time is quite useful for students in preparing for their exams. The solutions are simple, clear, and concise allowing students to understand them better. They can solve the practice questions and exercises that allow them to get exam-ready in no time.
You can get all the NCERT solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 from the official website of the Orchids International School. These solutions are tailored by subject matter experts and are very easy to understand.
Yes, students must practice all the questions provided in the NCERT solution for Class 7 Science Chapter 13: Motion and Time as it will help them gain a comprehensive understanding of the concept, identify their weak areas, and strengthen their preparation.
Students can utilize the NCERT solution for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 effectively by practicing the solutions regularly. Solve the exercises and practice questions given in the solution.

