Multiplication & Division for Grade 5 [+12 Worksheets]
This is a comprehensive lesson plan for teaching multiplication and division to grade 5 students. The lesson is designed to make the concepts easy and engage students with activities like real-life examples, quizzes, practice questions and worksheets.
Teachers can use this guide as a reference for delivering the concepts to students and engaging them in the classroom with the various questions and examples given on this page.
For parents, there are 12 downloadable practice worksheets that they can use for their kids.
In this article, students will learn:
-
Understand the concepts of multiplication and division and their properties.
-
Apply multiplication and division in real-life problem-solving.
-
Learn step-by-step methods to multiply and divide large numbers.
-
Master division with quotient and remainder.
-
Understand multiplication and division by 10, 100, and 1,000.
-
Solve word problems involving multiplication and division.
-
Improve speed and accuracy with multiplication and division tricks.
What is Multiplication?
Multiplication is one of the four basic mathematical operations used to find the total number of objects in equal-sized groups. It is often referred to as repeated addition because it allows us to add the same number multiple times quickly and efficiently.
For example, instead of adding 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 = 20, we can multiply 4 × 5 = 20.
Properties of Multiplication
-
Commutative Property – The order of numbers does not change the product.
-
example: 3 × 4 = 4 × 3 = 12
-
Associative Property – The grouping of numbers does not affect the product.
-
example: (2 × 3) × 4 = 2 × (3 × 4) = 24
-
Distributive Property – A number can be multiplied separately and then added.
-
example: 5 × (2 + 3) = (5 × 2) + (5 × 3) = 10 + 15 = 25
-
Multiplicative Identity – Any number multiplied by 1 remains the same.
-
example: 7 × 1 = 7
-
Multiplication by Zero – Any number multiplied by 0 is always 0.
-
example: 9 × 0 = 0
Multiplication of Large Numbers
When multiplying large numbers, the process is similar to multiplying smaller numbers but involves additional steps to keep track of place values and carrying over digits.
Steps for Multiplication
-
Write the numbers in columns, with the larger number on top.
-
Multiply the bottom number’s ones place with each digit of the top number.
-
Move to the tens place of the bottom number and multiply, adding a zero to the right.
-
Continue this process for the hundreds place, adding two zeros.
-
Add up all the intermediate results to get the final product.
Example: Multiply 246 × 32
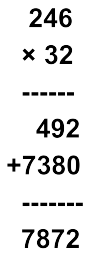
Thus, 246 × 32 = 7,872.
Multiplication by 10, 100, and 1,000
Multiplying a number by 10, 100, or 1,000 is easy because it simply involves adding zeros.
-
Multiplication by 10: Shift digits one place to the left, adding a zero at the end.
-
Multiplication by 100: Shift digits two places to the left, adding two zeros.
-
Multiplication by 1,000: Shift digits three places to the left, adding three zeros.
Examples:
245 × 10 = 2,450
245 × 100 = 24,500
245 × 1,000 = 2,45,000
What is Division?
Division is the process of splitting a number into equal parts. It is the opposite of multiplication.
For example, if we divide 24 cookies among 4 friends, each friend will get:
24 ÷ 4 = 6
Parts of a Division Problem
Dividend ÷ Divisor = Quotient (If any number is left, it is called the remainder)
For example:
35 ÷ 6 = 5
Remainder 5
Here, 35 is the dividend, 6 is the divisor, 5 is the quotient, and 5 is the remainder.
Division of Large Numbers
When dividing large numbers, long division is used to break the process into smaller steps.
Steps for Long Division
-
Write the dividend inside the division bracket and the divisor outside.
-
Divide the first digit of the dividend by the divisor.
-
Write the quotient on top and multiply it with the divisor.
-
Subtract the result from the dividend.
-
Bring down the next digit and repeat until all digits are divided.
Example: 6748 ÷ 26
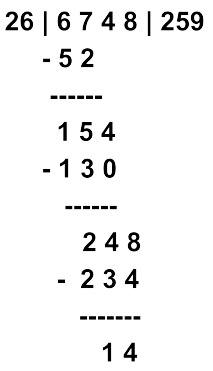
Thus, 6748 ÷ 26 = 259 with a remainder of 14
Division by 10, 100, and 1,000
Dividing by 10, 100, or 1,000 is the reverse of multiplication.
-
Division by 10: Remove one zero from the number.
-
Division by 100: Remove two zeros.
-
Division by 1,000: Remove three zeros.
Examples
3500 ÷ 10 = 350
3500 ÷ 100 = 35
3500 ÷ 1000 = 3.53
Real-life examples of Multiplication and Division
1. Grocery Shopping
A mother buys 5 packs of rice, and each pack contains 2 kg of rice.
Multiplication Used:
5 × 2 = 10 kg
The total rice she bought is 10 kg.
Now, she wants to divide the rice equally into 4 containers.
Division Used:
10 ÷ 4 = 2.5 kg per container
2. Planning a Party
You are hosting a birthday party with 8 guests. You want to give 3 cupcakes to each guest.
Multiplication Used:
8 × 3 = 248
You need to buy 24 cupcakes.
Later, you realize you only have 20 cupcakes and need to divide them equally among the guests.
Division Used:
20 ÷ 8 = 2.5 cupcakes per guest
3. Road Trip Fuel Calculation
A car consumes 5 liters of fuel every 100 km. You are planning a 600 km trip.
Multiplication Used:
5 × 6 = 30 liters
You need 30 liters of fuel for the journey.
If the fuel tank holds 60 liters, how many trips can be made before refueling?
Division Used:
60 ÷ 30 = 2 trips
4. Packing Chocolates in Boxes
A chocolate factory packs 12 chocolates in one box. They need to pack 600 chocolates.
Division Used:
600 ÷ 12 = 50 boxes
They need 50 boxes to pack all the chocolates.
If each box costs Rs. 10, what is the total cost of the boxes?
Multiplication Used:
50 × 10 = Rs. 500
5. Salary Calculation
A person earns Rs. 25,000 per month. How much will they earn in a year (12 months)?
Multiplication Used:
25,000 × 12 = 3,00,000
The person earns Rs. 3,00,000 per year.
If they want to save Rs. 1,20,000 in a year, how much should they save per month?
Division Used:
1,20,000 ÷ 12 = Rs. 10,000
They need to save Rs. 10,000 per month.
6. Sharing Pencils in a Classroom
A teacher has 45 pencils and needs to distribute them equally among 9 students.
Division Used:
45 ÷ 9 = 5
Each student will get 5 pencils.
If the teacher later buys 3 more pencils for each student, how many pencils are needed?
Multiplication Used:
9 × 3 = 27
She needs 27 additional pencils.
7. Buying Movie Tickets
A group of 6 friends goes to watch a movie. Each ticket costs Rs. 250.
Multiplication Used:
6 × 250 = Rs. 1500
The total cost for all tickets is Rs. 1500.
If they equally contribute the total amount, how much does each person pay?
Division Used:
1,500 ÷ 6 = Rs. 250
Each friend pays Rs. 250.
Fun Facts about Multiplication and Division
-
The multiplication table of 9 has a unique pattern (digits add up to 9).
-
Division by 1 leaves the number unchanged.
-
Multiplication and division are opposites (e.g., 6 × 4 = 24 and 24 ÷ 4 = 6).
Formula Chart
|
Operation |
Formula |
|
Multiplication |
Multiplicand × Multiplier = Product |
|
Division |
Dividend ÷ Divisor = Quotient |
|
Multiplication by 10 |
Number × 10 = Add one zero |
|
Multiplication by 100 |
Number × 100 = Add two zeros |
|
Multiplication by 1,000 |
Number × 1,000 = Add three zeros |
|
Division by 10 |
Number ÷ 10 = Remove one zero |
|
Division by 100 |
Number ÷ 100 = Remove two zeros |
|
Division by 1,000 |
Number ÷ 1,000 = Remove three zeros |
Orchids' Resources
Click the button to download the ebook on multiplication and division
Things You Have Learned
- Multiplication and Division are core mathematical operations.
- They help in problem-solving and daily calculations.
- Using shortcuts and formulas improves speed and accuracy.

