Two-Dimensional Shapes
2D shapes have two dimensions, namely height and width. Here, students will learn what 2D shapes and 2D shapes images are.
In this learning concept, the students will also learn to:
- Classify the 2d geometric shapes.
- Define the examples of 2d shapes.
- Identify the 2d shapes images.
Each concept is explained to class 4 maths students using illustrations, examples, and mind maps. Students can assess their learning by solving the two printable worksheets given at the page’s end.
Download the 2d shapes worksheet for class 4 and check the solutions to the 2d shapes questions for class 4 provided in PDF format.
Before we dive right in, let's meet the Founding Father of Geometry: Euclid

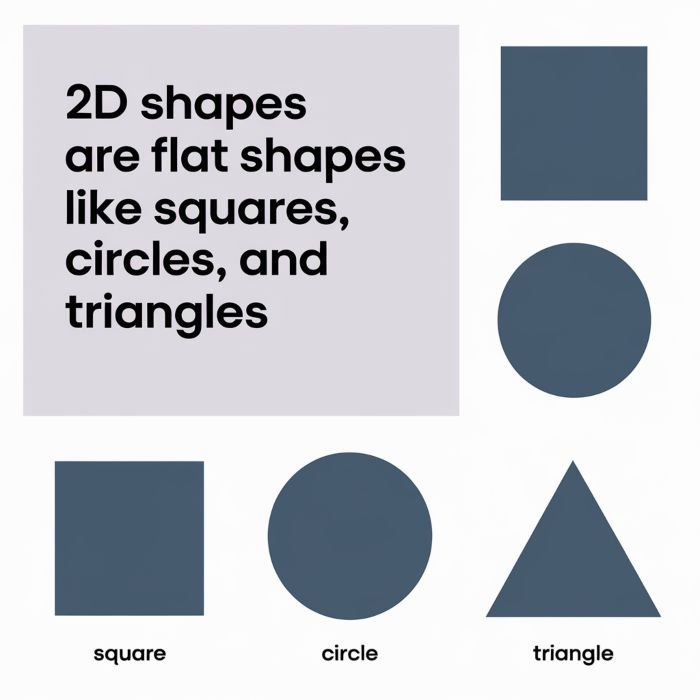
What Are 2D Shapes?
Did you notice that every object around you is of some shape? Some shapes are closed whereas some are open.

Did you observe the difference between the two shapes?
- Open: Have space in between
- Closed: No gaps in between
How to identify a 2D shape?
-
Count the Sides: How many straight edges (sides) does the shape have? For example, a square has 4 sides, and a triangle has 3.
-
Check the Angles: Are the corners (angles) sharp or curved? A square has 4 right angles (90°), but a circle has no angles at all.
-
Look at the Symmetry: Does the shape look the same if you fold it? Many shapes, like circles and squares, have symmetry.
-
Name the Shape: Once you know the sides, angles, and symmetry, you can usually figure out if it’s a square, triangle, circle, etc.
1. Plain Shapes
Two-Dimensional Shapes
-
Square: Four equal sides and four right angles (90°).
-
Rectangle: All sides are opposite congruent with four right angles.
-
Triangle: Three sides and three angles. It can be equilateral, isosceles or scalene.
-
Circle: A circular shape. No sides. Any point in this shape is equal distance from the center.
2. Solid Shapes
Three-Dimensional Shapes
-
Cube: All six faces are congruent squares with twelve edges and eight corners.
-
Sphere: It is a ball-shaped figure perfectly round, with no edges or vertices.
-
Cylinder: It has two round bases joined together with a curved surface.
-
Cone: A cone-shaped figure has a single vertex joined to a round base.
Observe the above picture and identify the plane and solid shapes:
2D GEOMETRIC SHAPES AND THEIR FEATURES:
1. Circle
-
Sides: 0 (it has no straight edges).
-
Corners: 0 (no vertices).
-
Features: All points on the circle are equidistant (the same distance) from the center.
-
Radius: The distance from the center to any point on the circle.
-
Diameter: A line segment that passes through the center and connects two points on the circle. The diameter is twice the length of the radius.
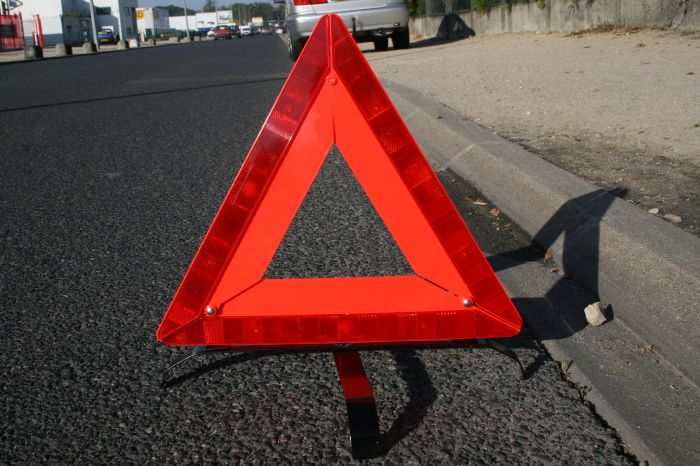
2. Triangle
- Sides: 3.
-
Corners/Vertices: 3.
-
Features: The sum of the interior angles of any triangle is always 180°.
-
Types of triangles based on side length:
Equilateral: All sides and angles are equal (each angle is 60°).
Isosceles: Two sides are equal in length, and the angles opposite these sides are equal.
Scalene: All sides and angles are different.
Example: A warning Sign Board

3. Square
-
Sides: 4 equal sides.
-
Corners/Vertices: 4.
-
Angles: 4 right angles (90°).
-
Features:
- Opposite sides are parallel and equal.
- All angles are right angles.
- Diagonals are equal in length and bisect each other at right angles.
Example: A photo frame
4. Rectangle
-
Sides: 4 (opposite sides are equal).
-
Corners/Vertices: 4.
-
Angles: 4 right angles (90°).
-
Features:
- Opposite sides are equal in length and parallel.
- Diagonals are equal in length but do not intersect at right angles.
Example: A book

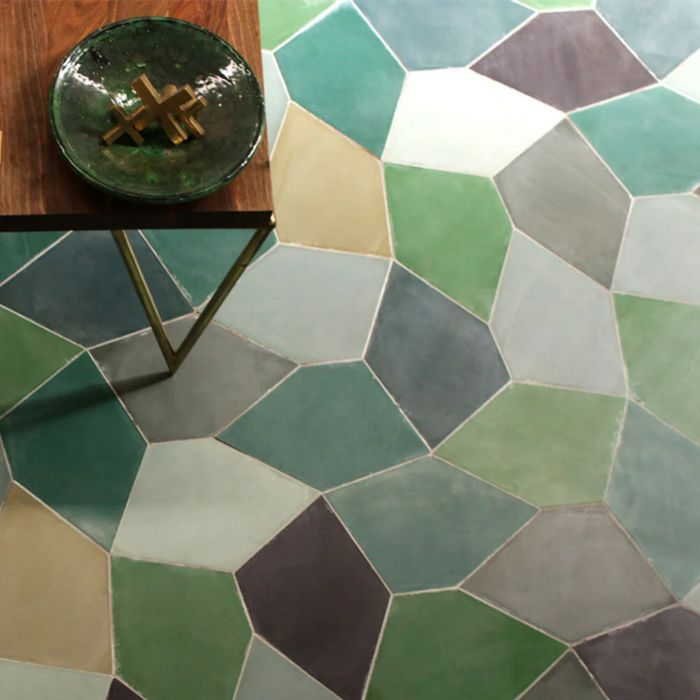
5. Pentagon
-
Sides: 5.
-
Corners/Vertices: 5.
-
Angles: The sum of the interior angles is 540°. Each angle in a regular pentagon is 108°.
- Features: A regular pentagon has five equal sides and angles, while an irregular pentagon can have sides and angles of different lengths and measures.
Example: Tiles (pentagon-shaped)

6. Hexagon
-
Sides: 6.
-
Corners/Vertices: 6.
-
Angles: The sum of the interior angles is 720°. Each angle in a regular hexagon is 120°.
-
Features: A regular hexagon has six equal sides and angles. It's often seen in nature (e.g., honeycomb patterns).
Example: A honeycomb

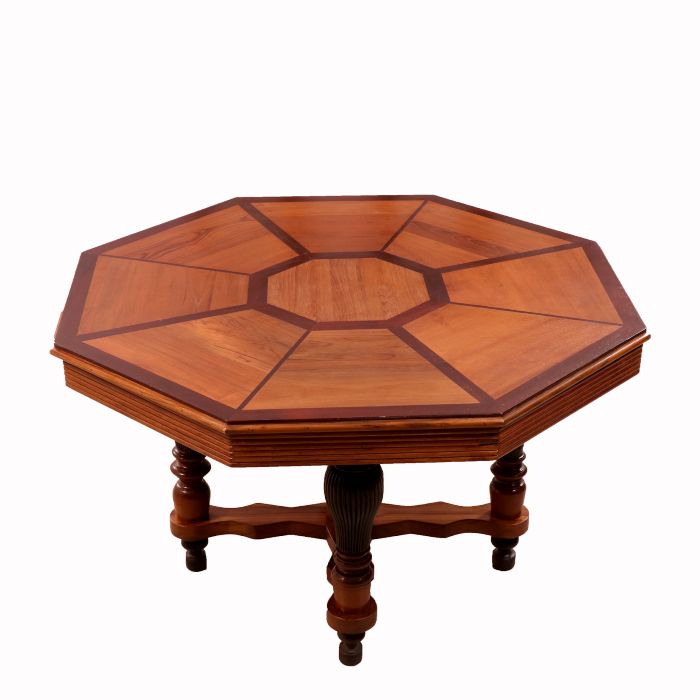
7. Octagon
-
Sides: 8.
-
Corners/Vertices: 8.
-
Angles: The sum of the interior angles is 1080°. Each angle in a regular octagon is 135°.
-
Features: A regular octagon has eight equal sides and angles. It is commonly seen in stop signs.
Example: A table

New words:
A figure which has 3 or more sides is called a polygon.

Quizzes For You
1. Which of the following shapes has 4 equal sides and 4 right angles?
a) Triangle
b) Rectangle
c) Square
d) Circle
2. How many sides does a hexagon have?
a) 5
b) 6
c) 7
d) 8
3. Which of these shapes has 4 sides, but only two parallel sides?
a) Square
b) Rectangle
c) Trapezoid
d) Parallelogram
4. What shape is commonly used for a stop sign?
a) Circle
b) Triangle
c) Octagon
d) Rectangle
5. Which of the following is NOT a 2D shape?
a) Rectangle
b) Square
c) Cube
d) Circle
6. What shape is used to represent a pizza?
a) Square
b) Triangle
c) Circle
d) Pentagon
7. Which of these shapes has all its sides the same length but does not have 90-degree angles?
a) Rectangle
b) Square
c) Rhombus
d) Circle
Practice Worksheets:
Click to download the worksheets for hands-on practice!
Easy Level Worksheets
Intermediate Level Worksheets
Advanced Level Worksheets

