Human Respiratory System - Diagram, Organs, Function
The breathing system helps us take in air. Breathing is super important because it gives us oxygen and removes carbon dioxide, which our body doesn’t need. Let’s see how it all works.
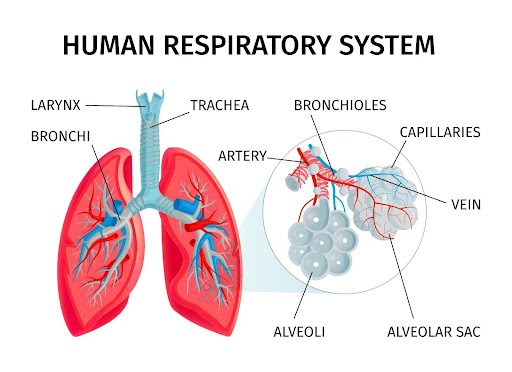
What is the Respiratory System?
The breathing system helps us take in air. Our body uses oxygen and pushes out carbon dioxide. If carbon dioxide stays inside, it can cause problems.
Components of the Respiratory System
To understand how we breathe, we need to understand the system that supports this process. Below is a summary of the key elements & how they work:
|
Part |
Function |
|
Nose/Nasal Cavity |
Filters, warms, & moistens the air we breathe. |
|
Pharynx (Throat) |
Connects the mouth and nasal cavity to the larynx & esophagus. |
|
Larynx (Voice Box) |
Produces sound and allows air to pass through to the trachea. |
|
Trachea (Windpipe) |
A tube that transports air from the larynx to the lungs. |
|
Bronchi |
Two branches carry air from the trachea into each lung. |
|
Lungs |
Main organs where oxygen is absorbed into the blood & carbon dioxide is removed. |
|
Bronchioles |
Smaller branches of the bronchi that distribute air within the lungs. |
|
Alveoli |
Tiny air sacs where the exchange of oxygen & carbon dioxide takes place. |
|
Diaphragm |
A muscle that helps pull air into the lungs & push it out during breathing. |
How Does Your Respiratory System Work?
There are two phases of breathing which are called inhalation & exhalation.
-
Inhalation (Breathing In)
-
Your diaphragm descends & contracts.
-
The thoracic cavity opens, letting air enter the lungs.
-
Air moves through the nose or mouth & down the tube to the lungs.
-
Exhalation (Breathing Out)
-
Diaphragm relaxation -> Go up.
-
A pull-down motion that compresses the chest cavity, expelling air from the lungs.
-
Carbon dioxide comes out through the nose or mouth.
The Mechanics of Out-Breathing: A Step-by-Step Process
-
Air enters the nose or mouth - It is filtered by tiny hairs & mucus in the nose.
-
Several passages through the pharynx and larynx - The air descends into the trachea.
-
Goes into the bronchi - The trachea branches into two bronchi, each entering a lung.
-
Spread through the bronchioles - The bronchi branch into smaller tubes known as bronchioles.
-
Reaches the alveoli - Oxygen from the air passes into the blood, and carbon dioxide from the blood enters the alveoli to be exhaled.
Importance of the Respiratory System
The respiratory system is necessary for the following:
-
Waste elimination: Exhaled carbon dioxide, waste product
-
Speaking: Air is pushed through the larynx & creates sounds.
Air Pollution and it's impact on respiratory system
One of the biggest threats faced by the respiratory system is air pollution. Dirty air carries harmful particles such as dust, smoke, and chemicals, which can injure the lungs.
Causes of Air Pollution
-
Emission by Vehicles: Cars, buses, and motorbikes release a large quantity of harmful gases.
-
Factories: Industrial processes discharge impurities.
-
Burning Waste: The smoke released by garbage burning adds a significant amount of pollution to the air.
-
Natural Causes: Volcano eruptions, wildfires contribute to pollution
The Effects of Air Pollution on the Respiratory System
-
Irritation: Air that is not clean can irritate the nose, throat & lungs.
-
Respiratory Infections: Germs in dirty air may lead to illness, including bronchitis or pneumonia.
-
Asthma: Air pollution can cause asthma attacks.
-
Long-Term Damage: Chronic lung diseases can be caused due to long-term exposure to pollution.
Prevention of Air Pollution
- Plant More Trees – Trees absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, making the air cleaner.
-
Use Public Transport or Cycle – Reduce car use by walking, cycling, or using buses and trains.
-
Save Electricity – Turn off lights, fans, and gadgets when not needed to reduce pollution from power plants.
-
Avoid Burning Waste – Burning garbage, especially plastic, releases harmful smoke. Always dispose of waste properly.
-
Spread Awareness – Educate friends and family about air pollution and ways to reduce it.
Common Respiratory Infections
Severe onsets can happen to anyone, and recurrent respiratory infections are peculiar to some badly polluted regions, even in cold/ wet weather.
Examples of Respiratory Infections
-
Common Cold: Viruses that cause stuffy nose, sneezing, coughing.
-
Bronchitis: Swelling of the bronchi, leading to coughing & shortness of breath.
-
Pneumonia: Infection in the lungs which, if untreated, can be serious.
-
Asthma: A condition where the airways become inflamed & narrowed, causing difficulty breathing.
Interesting Facts About the Respiratory System
-
Adults breathe around 12 to 16 times a minute; kids breathe even faster.
-
The total volume of air that can be occupied in the lungs is 6 liters.
-
The surface area of the alveoli in the lungs is approximately the size of a tennis court.
-
The right lung is a bit larger than the left lung.
How To Keep Our Lungs Healthy
Healthy lungs are a prerequisite for good health. Here are some things you can do to help keep them healthy:
-
Do Not Smoke: It can hurt their lungs & cause serious diseases.
-
Get Regular Exercise: Physical activities make the lungs stronger.
-
Eat Right: Healthy lungs need a solid eating routine.

