Geometry for Class 5 [+12 Practice Worksheets]
This is a comprehensive lesson plan for teaching geometry to grade 5 students. The lesson is designed to make the concepts easy and engage students with activities like quizzes, practice questions, worksheets and real-life examples.
Teachers can use this guide as a reference for delivering the concepts to students and engaging them in the classroom with the various questions and examples given in this page.
For parents, there are 12 downloadable practice worksheets that they can use for their kids.
In this article, you will learn:
- Understand basic geometry concepts such as points, lines, and angles.
- Identify and classify types of angles (acute, obtuse, right, straight, reflex, and complete angles).
- Differentiate between parallel lines, intersecting lines and perpendicular lines.
- Measure angles using a protractor.
- Recognize 2D and 3D shapes.
- Apply geometry in real-life situations.
Introduction to Geometry
Geometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with shapes, sizes, angles, and positions of objects. It helps us understand how different shapes interact with each other in space.
Basic Geometry Terms
Before we explore different geometrical concepts, let’s understand some basic terms:
|
Term |
Definition |
Example |
|
Point |
A location in space, represented by a dot. |
Tip of a pencil |
|
Line |
A straight path that extends infinitely in both directions. |
Horizon line |
|
Line Segment |
A part of a line with two fixed endpoints. |
Edge of a table |
|
Ray |
A line that starts from a point and extends infinitely in one direction. |
Sun’s rays |
|
Plane |
A flat surface that extends indefinitely in all directions. |
Surface of a blackboard |
Point:
Line:

Line Segment:

Ray:

Plane:
Practice Questions
-
Identify whether the given objects represent a point, line, line segment, ray, or plane:
-
Edge of a notebook
-
A light beam from a torch
-
The surface of a mobile screen
-
Name at least three objects from your surroundings that can be classified as line segments.
-
Draw a ray and label its parts correctly.
Types of Lines and Angles
Lines in Geometry
-
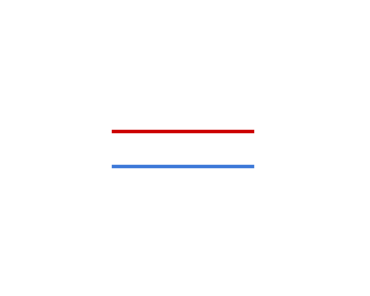
Parallel Lines: Lines that never meet and remain at the same distance apart.
-
Example: Railway tracks.
-
Notation: AB || CD
-
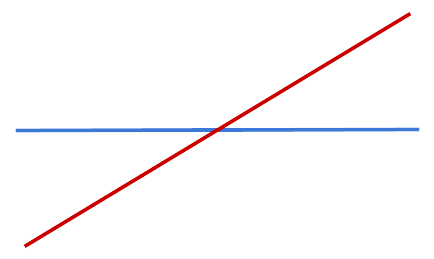
Intersecting Lines: Lines that cross each other at a single point.
-
Example: Scissors’ blades.
-
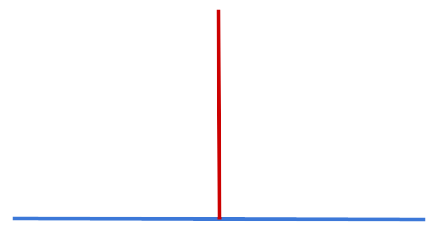
Perpendicular Lines: Lines that meet at a 90-degree angle.
-
Example: Corners of a book.
Parallel Lines:
Intersecting Lines:
Perpendicular Lines:
Practice Questions
-
Draw two parallel lines and two intersecting lines.
-
Give three real-life examples of parallel and perpendicular lines.
-
Can two intersecting lines be parallel? Explain why or why not.
Types of Angles
|
Type of Angle |
Measurement |
Example |
|
Acute Angle |
Less than 90° |
Pizza slice |
|
Right Angle |
Exactly 90° |
Corner of a square |
|
Obtuse Angle |
More than 90° but less than 180° |
Open book |
|
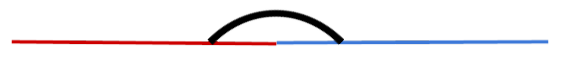
Straight Angle |
Exactly 180° |
Flat ruler |
|
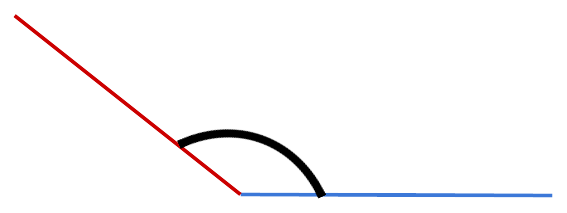
Reflex Angle |
More than 180° but less than 360° |
Ferris wheel rotation |
|
Complete Angle |
Exactly 360° |
Clock hands at 12:00 |
Acute angle:

Right Angle:
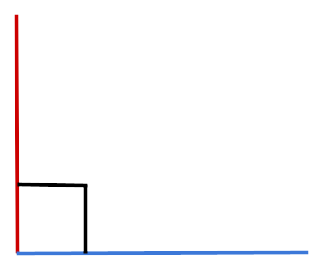
Obtuse Angle:
Straight Angle:
Reflex Angle:
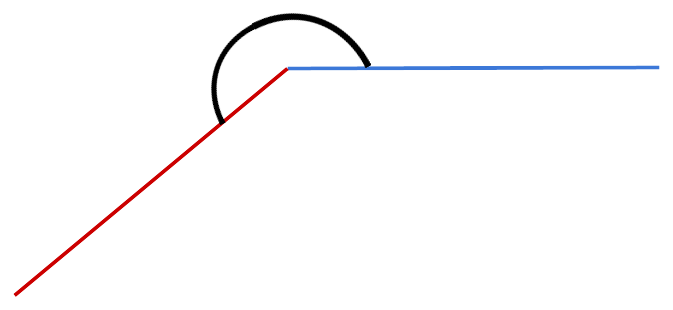
Complete Angle:
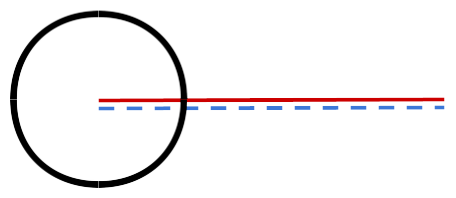
Practice Questions:
-
Identify the type of angles in the following:
-
Hands of a clock at 3:00
-
The top of a triangular road sign
-
An open book
-
Draw a right angle, obtuse angle, and acute angle.
-
Find an example of a reflex angle in real life.
Measuring Angles Using a Protractor
-
Place the center of the protractor on the vertex of the angle.
-
Align the baseline with one arm of the angle.
-
Read the degree where the second arm meets the protractor scale.
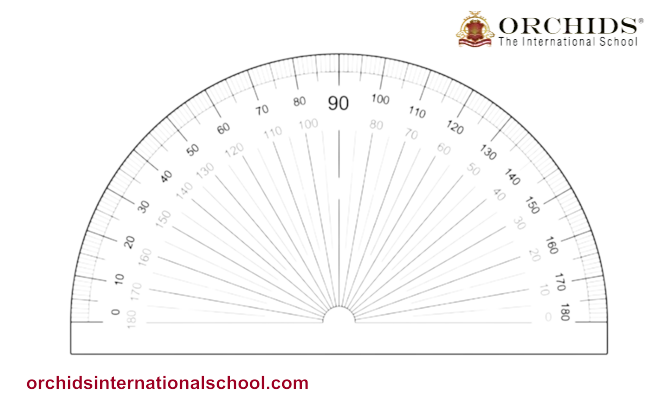
Practice Questions:
-
Measure an angle of 45°, 90°, and 120° using a protractor.
-
What would be the angle formed at 6:00 on a clock?
-
If an angle measures 70°, is it acute, obtuse, or right?
Real-Life Examples of Geometry
-
Buildings & Architecture – Houses are built using geometrical shapes like rectangles, triangles, and circles.
-
Sports & Games – Football fields, basketball courts, and cricket pitches all use geometry for markings.
-
Nature & Environment – Honeycombs are made of hexagonal shapes.
-
Transport & Roads – Traffic signs are in different geometric shapes (triangles, rectangles, circles).
-
Technology & Design – Mobile phones and laptops have rectangular screens with curved edges.
-
Art & Patterns – Designs in paintings, mandalas, and mosaic art use geometric patterns.
-
Everyday Objects – Objects like doors, windows, clocks, and even pizza slices follow geometric properties.
Fun Facts About Geometry
|
Fact |
Description |
|
Pi (π) Never Ends |
The value of π is 3.1415926535... and continues infinitely. |
|
Triangles are the Strongest Shapes |
Engineers use triangles in bridges for strength. |
|
A Circle has Infinite Lines of Symmetry |
Every diameter divides a circle into two equal halves. |
|
Rectangles Always Have Right Angles |
Every corner of a rectangle is 90°. |
|
Geometry is Used in Space |
Scientists use angles and distances to calculate planetary positions. |
Things you have learned!
- Basic Geometry Terms: Points, lines, angles, and shapes.
- Different Types of Angles: Acute, obtuse, right, straight, reflex, and complete.
- Parallel lines, Intersecting lines and Perpendicular lines
- Measuring Angles with a Protractor.
- Geometry in Real-Life Applications.
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities
- CBSE Schools in Bangalore
- CBSE Schools in Mumbai
- CBSE Schools in Pune
- CBSE Schools in Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools in Chennai
- CBSE Schools in Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools in Kolkata
- CBSE Schools in Indore
- CBSE Schools in Sonipat
- CBSE Schools in Delhi
- CBSE Schools in Rohtak
- CBSE Schools in Bhopal
- CBSE Schools in Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools in Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools in Jaipur
- CBSE Schools in Jodhpur
- CBSE Schools in Nagpur
- CBSE Schools in Ahmednagar
- CBSE School In Tumkur











