Importance of Water Conservation
1.Why Are Dams Built?
- Humans build dams over rivers which act as artificial water bodies.
- Dams have a massive reservoir where the river water can be stored and diverted in different areas apart from the river's route.
- Also, this water is used to produce hydroelectricity.

2.What Is the Importance of Groundwater? Why Is It Essential When It Is Not Readily Available for Use.
- Groundwater is a significant source of fresh water after rivers and lakes.
- The underground water is pumped with the help of bore wells and used for domestic and agricultural purposes.
- The level of groundwater affects the level of water in lakes and wells. The lower the groundwater level, the lower the water level in wells and lakes.

3.What Are the Causes of Water Pollution?
- Around 1500 substances in different forms are recorded as pollutants in freshwater.
- The water gets polluted due to the following factors:
- Waste and chemicals are released from industries and factories.
- Dumping of sewage and garbage in water bodies.
- Overuse of detergents and cleaning chemicals which washes off to the water bodies.
- Overuse of fertilisers and pesticides in agricultural fields, which, when reaching the water bodies, pollute them.

4. How Does Water From Farms and Sewage Pipelines Make the River Water Unfit? Does It Affect the Plants and Animals in the Water Bodies?
- The water from farms and sewage pipelines is full of chemicals and pollutants.
- These chemicals degrade the water quality in the water bodies, making it unsuitable for use.
- Also, due to fertilisers washed off, enormous water plants grow on the surface of the water leading to overconsumption of oxygen available in the water.
- It affects the animals in the water body and sometimes leads to migration or death.

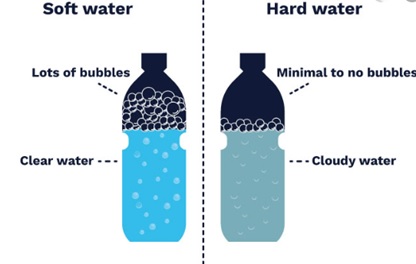
5.What Is ‘Hard Water’ and ’Soft Water?
- When the water contains a higher amount of minerals like calcium and magnesium in it, it is called hard water.
- Due to the presence of minerals, it tastes different.
- Soaps and detergents do not dissolve well in hard water; hence less foam is formed while using hard water. Underground water in some places is hard water.
- Soft water, however, contains very few or no minerals. It is mostly tasteless. Example: rainwater.
6.In Some Places, You Get Plenty of Water in Wells, but in Others, You Do Not Get Any. Explain Why.
- The level of water in wells depends on the level of underground water.
- In the areas with open grounds that are not covered with cemented coverings, the rainwater is absorbed well by the soil, leading to the recharging of the aquifer.
- On the other hand, the covering of bricks and cemented roads do not allow the water to seep down the soil, leading to a low groundwater level.
- Therefore, in some places, you get plenty of water in wells, but in others, you do not get any.

7.What Are the Effects of Flood?
The effects of floods are as follows:
- Loss of life and livestock.
- Damage to the crops.
- Scarcity of potable water.
- The onset of infectious diseases like diarrhoea and typhoid.
- The onset of infectious diseases like diarrhoea and typhoid.
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities
- CBSE Schools in Bangalore
- CBSE Schools in Mumbai
- CBSE Schools in Pune
- CBSE Schools in Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools in Chennai
- CBSE Schools in Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools in Kolkata
- CBSE Schools in Indore
- CBSE Schools in Sonipat
- CBSE Schools in Delhi
- CBSE Schools in Rohtak
- CBSE Schools in Bhopal
- CBSE Schools in Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools in Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools in Jaipur
- CBSE Schools in Jodhpur
- CBSE Schools in Nagpur
- CBSE Schools in Ahmednagar
- CBSE School In Tumkur











