Conservation of Forest and Wildlife
Forests and their importance:
- Forests are inhabited by the largest species of animals, birds, insects and plants. For the protection of wildlife, it is necessary that forest covers on the planet are conserved as they are home to an infinite number of living beings.
- An increase in the human population has led to more human activities in the forests,which has led to a drastic reduction in the global forest cover.
- The reasons behind the rapid loss of forest cover are—
- To obtain wood which is used as fuel, and also in making timber and furniture.
- To obtain raw materials for making paper.
- To increase agricultural lands as the demand for food rises due to the massive human population.
- To vacate land for making buildings, houses, industries, and roads.


Consequences of deforestation:
The cutting down of trees and clearance of forest cover is called deforestation. The different consequences of deforestation are—
- Shortage of wood and other forest products.
- Increase in temperature of the earth due to global warming.
- Plants play a significant role in bringing rainfall and absorbing carbon dioxide from the environment.
- Decrease in the forest cover has led to an increase in the level of carbon dioxide, which in turn has altered the temperature of our planet.
- It has happened because carbon dioxide is a heat-absorbing gas.
- Increase in soil erosion, which lead to soil infertility and desertification.
- The roots of the plants hold the soil and do not allow the top fertile soil layer to get carried away or washed away by natural forces like wind and water.
- Cutting trees on a large scale makes the fertile topsoil prone to erosion by natural forces like wind and water, thereby decreasing the soil fertility.
- It affects the water cycle in the environment and decreases the frequency of occurrence of rainfall. As a result, the groundwater level also decreases gradually.
- Extinction of wild animals and plants.
- Wild animals and plants depend on the forests for their survival. Deforestation forces the animals to move to different areas that are near to the human population or are not favourable for their survival. So, they either do not survive or get killed.
- The absence of forest cover decreases the availability of food for animals, due to which they are starved to death.



Protected areas for the conservation of wildlife
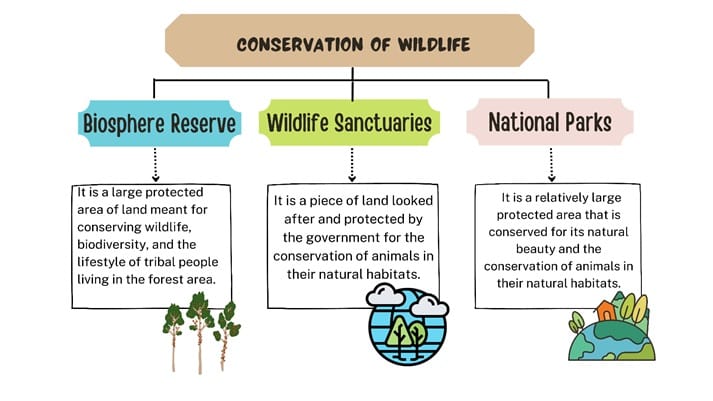
- Biosphere reserves:
- It is a large protected area of land meant for conserving wildlife, biodiversity, and the lifestyle of tribal people living in the forest area.
- The tribal people are an integral part of the biosphere reserves, making them unique.
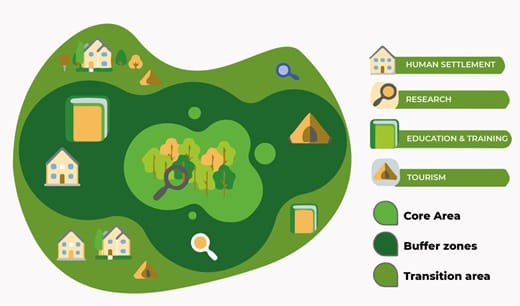
- A biosphere reserve can be divided into three areas—
- Core: It is the innermost area, which is completely dedicated to the wildlife, and no human intervention is allowed in this zone.
- Middle/Buffer zone: It is a specifically marked region where human activities like research and educational tours are allowed.
- Outermost/transition zone: The area where the tribals live and activities that would not harm the wildlife are allowed.
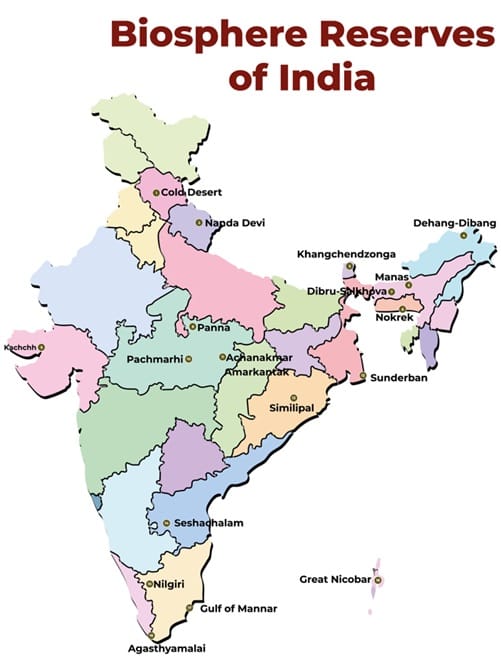
Some of the famous biosphere reserves of India are as follows—
| Name | State |
| Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve | Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
| Kaziranga Biosphere Reserve | Assam |
| Sunderbans Biosphere Reserve | West Bengal |
| Kanha Biosphere Reserve | Madhya Pradesh |
| Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve | Madhya Pradesh |
Role of a Biosphere Reserve:
-
- Helps in the conservation and maintenance of wildlife in that area.
- Assists in research and development related to biodiversity.
- Helps the tribal to preserve their traditions and lifestyle.
- Wildlife Sanctuary:
- It is a piece of land looked after and protected by the government for the conservation of animals in their natural habitats.
- No hunting and poaching are allowed in these areas.
- Human activities are banned in these areas.
- Some of the threatened species protected in the different wildlife sanctuaries of India are the blackbuck, elephant, golden-headed duck, gharial, python, and rhinoceros.
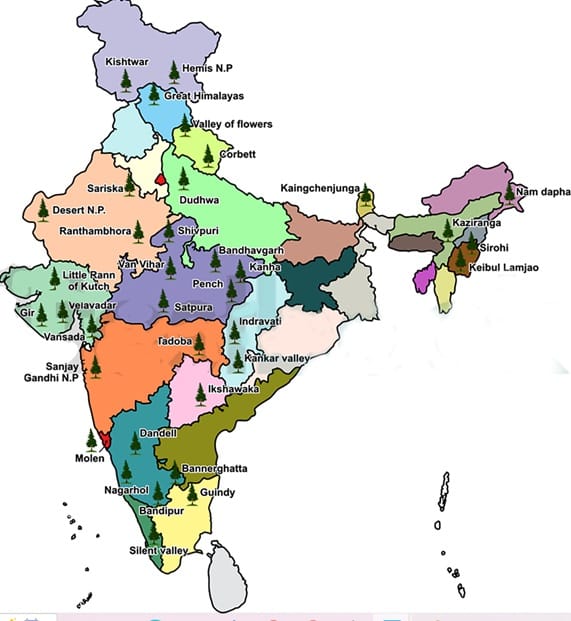
Some major wildlife sanctuaries of India are as follows—
Name State Sanjay Gandhi Wildlife Sanctuary Maharashtra Nagarjunasagar Wildlife Sanctuary Andhra Pradesh Bharatpur Wildlife Sanctuary Rajasthan Sultanpur Wildlife Sanctuary Haryana Dandeli Wildlife Sanctuary Karnataka Thattekad Wildlife Sanctuary Kerala Satkosia Wildlife Sanctuary Odisha Lockchao Wildlife Sanctuary Manipur Bori Wildlife Sanctuary Madhya Pradesh - National Parks:
- It is a relatively large protected area that is conserved for its natural beauty and the conservation of animals in their natural habitats.
- These areas are open for recreation and tours.
- The primary objective of a national park is to provide a safe environment for wildlife. Human activities like hunting, mining, and fishing are not allowed.
- India has more than 80 national parks.
- Some national parks are famous for their exclusive resources and animal species.
Examples:
Satpura National Park has the finest teak available. Also, the rock paintings at the Satpura National Park are a major source of tourist attraction.
Some famous national parks of India are as follows—
Name State Animals protected Jim Corbett National Park Uttarakhand Tiger, Elephants, Crocodile, Deer, Leopards, Gharials Kanha National Park Madhya Pradesh Bengal Tiger, Barasingha, Sloth bear Ranthambore National Park Rajasthan Tiger, Panther, Bear, Sambhar Gir National Park Gujarat Lion, Jackals, Leopards, Deer, Crocodiles Kaziranga National Park Assam Rhinoceros, Bengal tiger, Asian Elephant Sunderbans National Park West Bengal Bengal Tiger, Crocodile, Ganges River Dolphin, Horseshoe crab Bandipur National Park Karnataka Mugger crocodile, Indian rock python, Golden jackal, sloth bear Dachigam National Park Jammu Kashmir Musk Deer, Snow leopard, Kashmir langur, Himalayan black bear Sariska National Park Rajasthan Nilgai, Jungle cat, Hyena, Leopard, Four-horned antelope Satpura National Park Madhya Pradesh Sloth bear, Crocodile, Four-horned antelope, Otters, Langurs
New Words
Traditions: These are the customs and beliefs that are transferred from one generation to another.
Threatened species: Species that are vulnerable of getting endangered in the near future.
Erosion: Wearing away of the soil by natural forces like water, wind and ice.
Did You Know?
- Hemis National Park in Jammu and Kashmir is the largest National Park in India.
- Madhya Pradesh and Andaman and Nicobar Islands have the highest number of national parks, totalling nine each.
- Hailey National Park was the first to be declared a national park of India in 1936, now known as the Jim Corbett National Park.
- Kaziranga, Manas, and Keoladeo National Parks are declared World Heritage Sites by UNESCO.
- The First National marine park of India is situated in the Gulf of Kutch, known as Marine National Park.
Share

