Components of Food - Nutrients, Examples & More for Class 6
Nutrition refers to how components of food are processed by our body. Food is composed of essential nutrients that helps our body to do its normal functions. Food is the most important source of nutrients and nutrients have a key role for the improvement of life.
Important components of food are as follows:
-
Carbohydrates
-
Fats
-
Proteins
-
Vitamins
-
Minerals
-
Roughage (Dietary Fiber)
-
Water
These nutrients are essential to support our movement and health. But when you don’t have one of them, you can have health problems.

Food Groups
Food can be divided into three groups based on their functions:
|
Food Group |
Function |
Examples |
|
Energy-Giving Foods |
Provide energy for the body |
Rice, bread, potatoes, sugar, fats |
|
Body-Building Foods |
Help in growth and repair |
Meat, fish, beans, eggs, nuts, tofu |
|
Protective Foods |
Protect against diseases |
Fruits, vegetables, dairy, vitamins, minerals |
Eating a balanced mix of all three types of components of food ensures proper growth and development.
Carbohydrates
The chief source of energy for our body is carbohydrates. There are two types:
-
Simple Carbohydrates: Present in sugar, fruits, and milk. They are called simple sugars because they are quickly digested and provide instant energy.
-
Complex Carbohydrates: Present in bread, rice and potatoes. They digest slowly and give sustained energy.
Functions of Carbohydrates
-
Provide quick energy.
-
Help in brain function.
-
Crucial for exercising.
-
Maintain blood sugar levels.
-
Build better digestion and gut health - when you get it from fiber-dense foods
Fun Fact: The natural sugars in bananas provide instant energy, so athletes love this food.
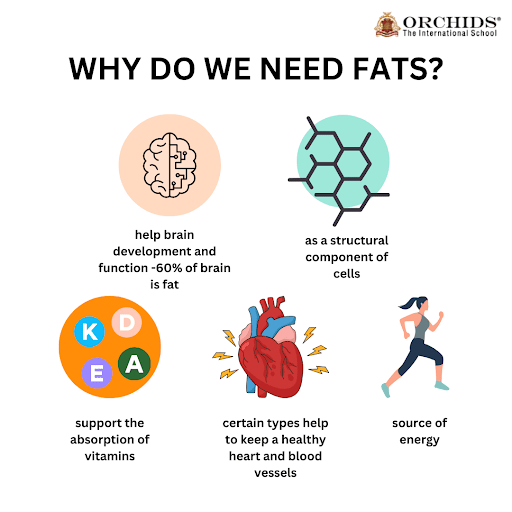
Fats
Fats give more energy than carbohydrates and assist in energy storage in the human body. They are of two types:
Vegetable Fats: Found in nuts, olive oil and sunflower oil. These fats tend to be healthier.
Animal Fats: Animal fats such as butter, ghee and meat. But too much of anything can be bad for you.
Functions of Fats
-
Store energy for future use.
-
Keep our body warm.
-
Protect organs from injury.
-
Helps absorb fat-soluble vitamins: A, D, E and K.
-
Role in cell growth and in hormone production.
Fun Fact: Whales have a fatty layer called blubber that keeps them warm in cold water.
Proteins
Proteins help build up and replenish the body. They are found in:
-
Plant Sources: Beans, lentils, nuts, soy products like tofu.
-
Animal sources: meat, fish, eggs, milk, cheese
Functions of Proteins
-
Specialized in the synthesis and recovery of the muscles.
-
Repair body tissues.
-
Make enzymes and hormones.
-
Strengthen immune system.
-
Help in cell regeneration.
Vitamins and Minerals
For the survival of the body and to keep it disease free and healthy, vitamins and minerals are required. Vitamin types are:
-
Vitamins Fat-Soluble: A,D,E and K (in our bodies and fatty foods)
-
Water-soluble: B-complex, C (must be taken daily, since they dissolve in water)
List of Common Vitamins:
|
Vitamin |
Function |
Sources |
|
Vitamin A |
Good for eyesight |
Carrots, spinach, sweet potatoes |
|
Vitamin C |
Helps heal wounds and boosts immunity |
Oranges, lemons, strawberries |
|
Vitamin D |
Strengthens bones and teeth |
Sunlight, milk, fish |
|
Vitamin E |
Helps skin and hair health |
Nuts, seeds, spinach |
|
Vitamin K |
Helps in blood clotting |
Green leafy vegetables, broccoli |
|
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) |
Helps the body convert food into energy. Supports the nervous system and muscle function. |
Whole grains (like brown rice, oats), Pork, Beans, Nuts |
|
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) |
Helps produce energy from food. Maintains healthy skin, eyes, and nervous system. |
Milk and dairy products, Eggs, Leafy greens (like spinach), Almonds |
|
Vitamin B3 (Niacin) |
Helps the body convert food into energy. Supports the health of the skin, nerves, and digestive system. |
Poultry (chicken, turkey), Fish (like tuna, salmon), Whole grains, Peanuts |
|
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) |
Helps produce energy from food. Supports the production of hormones and red blood cells. |
Chicken, Eggs, Whole grains, Avocados |
|
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) |
Helps the body make red blood cells. Supports brain function and immune system. |
Fish (salmon, tuna), Poultry, Potatoes, Bananas |
|
Vitamin B7 (Biotin) |
Helps convert food into energy. Supports healthy hair, skin, and nails. |
Eggs, Nuts, Legumes (beans, lentils), Whole grains |
|
Vitamin B9 (Folate or Folic Acid) |
Essential for cell division and growth. Helps prevent birth defects during pregnancy. |
Leafy greens (spinach, kale), Beans and lentils, Citrus fruits (oranges, lemons), Avocados |
|
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) |
Helps produce red blood cells. Supports the nervous system and brain function. |
Meat (beef, pork), Fish and shellfish (salmon, shrimp), Dairy products, Eggs |
List of Common Minerals:
|
Mineral |
Function |
Sources |
|
Calcium |
Strong bones and teeth |
Milk, cheese, leafy greens |
|
Iron |
Helps in blood formation |
Spinach, red meat, lentils |
|
Potassium |
Maintains blood pressure and muscle function |
Bananas, potatoes, avocados |
|
Zinc |
Boosts immune system |
Nuts, dairy, seafood |
Roughage and Water
Fruits, vegetables, whole grains and nuts - Roughage (Dietary Fibre). It helps in digestion.
Importance of Roughage:
-
Prevents constipation.
-
Maintains healthy digestion.
-
Controls blood sugar levels.
-
Less prone to heart diseases.
-
Keep the weight in check.
Water: Water is very important for all living things, including humans. Our bodies are made up of about 60% water, and we need it to stay healthy. Water helps our bodies work properly in many ways.
Functions of Water:
-
Helps in digestion.
-
Maintains body temperature.
-
Removes waste from the body.
-
Carries nutrients and oxygen to cells.
-
No dehydration and fatigue.
Fun Fact: Watermelon is 92% water, so it’s basically the perfect summer fruit.
Balanced Diet
A balanced diet means eating the right kinds of food in the right amounts to stay healthy. It includes different foods that give us the nutrients we need, like vitamins, minerals, proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Eating a variety of foods in the right amounts helps us stay energetic, grow well, and stay strong.
Here are the sources of an Indian balanced diet:
Carbohydrates (Energy): Rice, Chapati (roti), Paratha, Dosa
Proteins (Growth and Repair): Lentils (dal), Beans (rajma, chana), Paneer (cottage cheese), Chicken, Fish, Eggs
Healthy Fats (Energy and Healthy Cells): Ghee, Butter, Mustard oil, Olive oil, Coconut oil, Nuts (almonds, cashews), Seeds (flaxseeds, sunflower seeds)
Vitamins and Minerals (Body Function and Immunity): Vegetables (spinach, carrots, cauliflower, peas, tomatoes), Fruits (mango, banana, apples, oranges, pomegranate), Dairy products (milk, yogurt)
Fiber (Digestion and Healthy Gut): Whole grains (brown rice, whole wheat flour), Vegetables (spinach, broccoli, carrots), Fruits (apples, oranges, bananas), Legumes (dal, peas)
Water (Hydration): Water, Buttermilk, Fresh fruit juice, Tea

"Click to unlock the secret powers of fruits and veggies!"
Example of an Indian Balanced Diet Meal
Breakfast:
-
Vegetable Upma or Poha (Carbohydrates + Vegetables + Fiber)
-
Buttermilk or a glass of fresh fruit juice (Hydration + Vitamins)
Lunch:
-
Chapati or Rice (Carbohydrates)
-
Dal Tadka (Lentils for protein)
-
Vegetable Sabzi (Mixed vegetables like spinach, beans, carrots for vitamins and minerals)
-
Cucumber or tomato salad (For fiber)
-
Curd (Yogurt) (For probiotics and calcium)
-
Water (Hydration)
Dinner:
-
Chapati or Brown Rice (Carbohydrates)
-
Paneer Curry or Chicken Curry (Protein from paneer or meat)
-
Steamed Vegetables (Fiber + Vitamins)
-
Raita (yogurt mixed with cucumber) (For probiotics)
-
A glass of water or Herbal tea (Hydration)
All food materials, a balanced diet means we get all nutrients in proper proportions required by us for being healthy. It protects from malnutrition and deficiency diseases like:
-
Kwashiorkor (Protein Deficiency):
Symptoms - Swollen belly, fatigue and poor growth -
Marasmus (Protein-energy malnutrition):
Symptoms - Severe thinness and weakness, retarded growth -
Rickets (Vitamin D Deficiency):
Symptoms - Bowed legs, bones weak. -
Anemia (Iron deficiency):
Symptoms - Weakness, you become pale skin.
"Let’s learn how to make your tummy happy – read the blog now!"
Things you have learned!
- Food are any substances consumed by living organisms, including humans, that provide essential nutrients, comprising carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, roughage, and water.
- A balanced diet includes the right proportions of a variety of foods.
- Fat/carbs provide energy, protein for growth, vitamins/minerals help keep us healthy.
- Roughage and water are needed to digest properly and keep a healthy body.
- Nutritional deficiencies can also lead to conditions such as kwashiorkor, anemia and rickets.

