NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Geography Chapter - 3 Drainage
Orchids International School strives to give learners in-depth knowledge of all the crucial topics, including Drainage, covered in Class 9 Geography Chapter 3. We support this by our well-developed NCERT solutions whereby students will be able to gain insight into the intricacies of drainage systems and their importance. The content is made interesting and easy to comprehend, making learning a joy rather than a chore.
Download PDF For NCERT Solutions for SST-Geography Drainage
The NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Geography Chapter - 3 Drainage are tailored to help the students master the concepts that are key to success in their classrooms. The solutions given in the PDF are developed by experts and correlate with the CBSE syllabus of 2023-2024. These solutions provide thorough explanations with a step-by-step approach to solving problems. Students can easily get a hold of the subject and learn the basics with a deeper understanding. Additionally, they can practice better, be confident, and perform well in their examinations with the support of this PDF.
Download PDF
Access Answers to NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Geography Chapter - 3 Drainage
Students can access the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Geography Chapter - 3 Drainage. Curated by experts according to the CBSE syllabus for 2023–2024, these step-by-step solutions make SST-Geography much easier to understand and learn for the students. These solutions can be used in practice by students to attain skills in solving problems, reinforce important learning objectives, and be well-prepared for tests.
Drainage
Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below.
i). In which of the following states is the Wular lake located?
-
Rajasthan
-
Uttar Pradesh
-
Punjab
-
Jammu and Kashmir
ii). The river Narmada has its source at
-
Satpura
-
Brahmagiri
-
Amarkantak
-
Slopes of the Western Ghats
iii). Which one of the following lakes is a salt water lake?
-
Sambhar
-
Dal
-
Wular
-
Gobind Sagar
iv). Which one of the following is the longest river of the Peninsular India?
-
Narmada
-
Krishna
-
Godavari
-
Mahanadi
v). Which one amongst the following rivers flows through a rift valley?
-
Mahanadi
-
Tungabhadra
-
Krishna
-
Tapi
i). (d) Jammu and Kashmir
ii). (c) Amarkantak
iii). (a) Sambhar
iv). (c) Godavari
v). (d) Tapi
Answer the following questions briefly.
i). What is meant by a water divide? Give an example.
ii). Which is the largest river basin in India?
iii). Where do the rivers Indus and Ganga have their origin?
iv). Name the two headstreams of the Ganga. Where do they meet to form the Ganga?
v). Why does the Brahmaputra in its Tibetan part have less silt, despite a longer course?
vi). Which two Peninsular rivers flow through trough?
vii). State some economic benefits of rivers and lakes.
i). A mountain range or a hill separating two different drainage basins is called a water divide. For example, Western Ghats.
ii). The Ganga river basin is the largest river basin in India.
iii). The Indus river has its origins in Tibet near the Mansarovar Lake while the Ganga River has its origins in the Gangotri Glacier in Uttarakhand state.
iv). Alaknanda and Bhagirathi are the two headstreams of the Ganga. They both meet to form the Ganga at Devprayag.
v). The Brahmaputra river also known as Tsangpo in Tibet receives very little volume of water in Tibet so it carries little silt there. But once it enters into India from Arunachal Pradesh, it is fed by lots of rains and hence carries lots of water and silt.
vi). The two rivers that flow through troughs in India are Narmada and Tapi. They form estuaries while entering the sea unlike deltas.
vii). Rivers are very beneficial for agricultural purposes and generating hydro- electricity. They also provide fisheries and inland channels for transportation. The lakes like the Sambhar Lake provide edible salts to people. They also help to develop tourism and provide recreation for people such as Panging Tso.
Below are given names of a few lakes of India. Group them under two categories – Natural and created by human beings.
-
Wular
-
Dal
-
Nainital
-
Bhimtal
-
Gobind Sagar
-
Loktak
-
Barapani
-
Chilika
-
Sambhar
-
Rana Pratap Sagar
-
Nizam Sagar
-
Pulicat
-
Nagarjuna Sagar
-
Hirakud
The Natural Lakes are: Wular, Dal, Nainital, Bhimtal, Chilika, Pulicat, Sambhar, Barapani, Loktak.
The Lakes created by human beings are: Gobind Sagar, Hirakud, Rana Pratap Sagar, Nagarjuna Sagar, Nizam Sagar.
Discuss the significant difference between the Himalayan and the Peninsular rivers.
The following is the comparison of the two rivers:
|
S. No. |
Himalayan Rivers |
Peninsular Rivers |
|
1 |
Himalayan rivers are perennial. |
Peninsular rivers are seasonal. |
|
2 |
They are fed by glaciers. |
They receive water from the rainfall. |
|
3 |
The Himalayan rivers are long and deep. |
The peninsular rivers are short and shallow. |
|
4 |
They carry a lot silt and sand. |
They carry very no silt. |
|
5 |
These rivers originate in the Himalayas in northern India. |
These rivers originate in the Western Ghats. |
|
6 |
Their drainage basins are large. |
Their drainage basins are small. |
|
7 |
These rivers form very large deltas. |
They form very small or no deltas. |
Compare the east flowing and the west flowing rivers of the Peninsular plateau.
The following is the comparison of the two rivers:
|
S. No. |
East Flowing Rivers |
West Flowing Rivers |
|
1. |
They fall into the Bay of Bengal. |
They fall into the Arabian Sea. |
|
2. |
They form Estuaries |
They form Deltas. |
|
3. |
They have a large tributary network. |
They have no tributary networks. |
|
4. |
They do not flow through troughs. |
They flow through troughs. |
(i) Why are rivers important for the country’s economy?
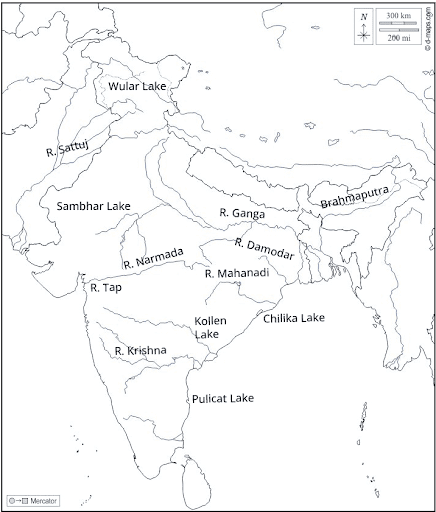
(ii) On an outline map of India mark and label the following rivers: Ganga, Satluj, Damodar, Krishna, Narmada, Tapi, Mahanadi, and Brahmaputra.
(iii) On an outline map of India mark and label the following lakes: Chilika Sambhar, Wular, Pulicat, Kolleru.
i) The rivers important for the any country’s economy because:
-
They are a source of natural fresh water which is required for the survival of all living beings.
-
The rivers provide water for various purposes as well as act as important trade routes within the country.
-
They also serve as a source of potential energy using hydro power.
-
It is also used for navigation and transportation and is important for commercial activities.
-
It also provides great scenic and recreational values for tourism. Thus, they serve as good tourist spots in the state.
Frequently Asked Questions
The NCERT solution for Class 9 Chapter 3: Drainage is important as it provides a structured approach to learning, ensuring that students develop a strong understanding of foundational concepts early in their academic journey. By mastering these basics, students can build confidence and readiness for tackling more difficult concepts in their further education.
Yes, the NCERT solution for Class 9 Chapter 3: Drainage is quite useful for students in preparing for their exams. The solutions are simple, clear, and concise allowing students to understand them better. They can solve the practice questions and exercises that allow them to get exam-ready in no time.
You can get all the NCERT solutions for Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 from the official website of the Orchids International School. These solutions are tailored by subject matter experts and are very easy to understand.
Yes, students must practice all the questions provided in the NCERT solution for Class 9 Geography Chapter 3: Drainage as it will help them gain a comprehensive understanding of the concept, identify their weak areas, and strengthen their preparation.
Students can utilize the NCERT solution for Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 effectively by practicing the solutions regularly. Solve the exercises and practice questions given in the solution.

