NCERT Class 9 Science (Chemistry) Chapter 1 – Matter in Our Surroundings
The first chapter, "Matter in Our Surroundings," of Class 9 Science introduces students to some of the basic concepts of matter and its different states. Our NCERT solutions provide a gradual, step-by-step method to understand this chapter and hence ensure that students would formulate a proper grasp of the core principles and applications of matter and its surroundings.
Download PDF For NCERT Solutions for Science Matter in Our Surroundings
The NCERT Class 9 Science (Chemistry) Chapter 1 – Matter in Our Surroundings are tailored to help the students master the concepts that are key to success in their classrooms. The solutions given in the PDF are developed by experts and correlate with the CBSE syllabus of 2023-2024. These solutions provide thorough explanations with a step-by-step approach to solving problems. Students can easily get a hold of the subject and learn the basics with a deeper understanding. Additionally, they can practice better, be confident, and perform well in their examinations with the support of this PDF.
Download PDF
Access Answers to NCERT Class 9 Science (Chemistry) Chapter 1 – Matter in Our Surroundings
Students can access the NCERT Class 9 Science (Chemistry) Chapter 1 – Matter in Our Surroundings. Curated by experts according to the CBSE syllabus for 2023–2024, these step-by-step solutions make Science much easier to understand and learn for the students. These solutions can be used in practice by students to attain skills in solving problems, reinforce important learning objectives, and be well-prepared for tests.
Exercise-1.1
Which of the following are matter?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, lemon water, the smell of perfume.
The following substances are matter:
Chair
Air
Almonds
Lemon water
The smell of perfume (Smell is considered as a matter due to the presence of some volatile substances in air that occupy space & have mass.)
Give reasons for the following observation:
The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several meters away, but to get the smell from cold food, you have to go close.
Particles in the air, if fueled with higher temperatures, acquire high kinetic energy, which aids them to move fast over a stretch. Hence, the smell of hot sizzling food reaches a person even at a distance of several meters.
A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. Which property of matter does this observation show?
The diver is able to easily cut through the water in the swimming pool because of the weak forces of attraction between water molecules. It is this property of water that attributes to easy diving.
What are the characteristics of the particles of matter?
The characteristics of particles of matter are as follows:
(a) Presence of intermolecular spaces between particles
(b) Particles are in constant motion
(c) They attract each other
(d) All matter is composed of very small particles which can exist independently.
Exercise-1.2
The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density. (density=mass/volume). Arrange the following in the order of increasing density – air, exhaust from the chimneys, honey, water, chalk, cotton and iron.
The following substances are arranged in increasing density:
Air
Exhaust from chimney
Cotton
Water
Honey
Chalk
Iron
Answer the following.
a) Tabulate the differences in the characteristics of matter.
b) Comment upon the following: rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy and density.
(a) The difference in the characteristics of the three states of matter.
|
Characteristics |
Solid |
Liquid |
Gas |
|
Shape |
Fixed shape |
No Fixed shape |
No Fixed shape |
|
Volume |
Fixed volume |
Fixed volume |
No Fixed volume |
|
Intermolecular force |
Maximum |
Less than solids |
Very less |
|
Intermolecular space |
Very less |
More than solids |
maximum |
|
Rigidity/Fluidity |
Rigid/cannot flow |
Can flow/not rigid |
Can flow/not rigid |
|
Compressibility |
negligible |
compressible |
Highly compressible |
(b) (i) Rigidity: It is the property of matter to continue to remain in its shape when treated
with an external force.
(ii) Compressibility: It is the attribute of the particles to contract their intermolecular space when
exposed to an external force, thereby escalating its density.
(iii) Fluidity: It is the ability of a substance to flow or move about freely.
(iv) Filling the gas container: The particles in a container take their shape as they randomly vibrate in all possible directions.
(v) Shape: It is the definite structure of an object within an external boundary
(vi) Kinetic energy: Motion allows particles to possess energy which is referred to as kinetic energy. The increasing order of kinetic energy possessed by various states of matter are:
Solids < Liquids < Gases
Mathematically, it can be expressed as K.E = 1/2 mv2, where ‘m’ is the mass and ‘v’ is the velocity of the particle.
(vii) Density: It is the mass of a unit volume of a substance. It is expressed as:
d = M/V, where ‘d’ is the density, ‘M’ is the mass and ‘V’ is the volume of the substance
Give reasons
a) A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept.
b) A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
c) A wooden table should be called a solid.
d) We can easily move our hand in the air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
(a) There is a low force of attraction between gas particles. The particles in the filled vessel are free to move about.
(b) Gaseous particles have the weakest attraction force. They are always moving in a haphazard manner. When a gas particle collides with the container’s walls, it exerts force and, thus pressure on the wall.
(c) There is a distinct contour and volume to the hardwood table. The wood particles are tightly packed. They do not conform to the container’s shape. As a result, the solid features of a hardwood table are satisfied.
(d) The boundaries between air particles are quite loose. They are a long way apart and have a lot of space between them. As a result, we may move our hands freely in the air. The particles in a solid block, on the other hand, are bound together by a strong force of attraction. As a result, there is either some or no space between them. As a result, we will require a karate expert.
Liquids generally have a lower density than solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why.
In general, the volume of a liquid is more than the volume of a solid because liquid particles are freer to move, resulting in more volume. Ice, on the other hand, has a maximum density of water at 4 degrees Celsius. Ice is lighter than water and has a lower density. As a result, it floats on water.
Exercise – 1.3
Convert the following temperature to Celsius scale:
a. 300K b. 573K
a. 0°C=273K
300K= (300-273)°C = 27°C
b. 573K= (573-273)°C = 300°C
What is the physical state of water at:
a. 250°C b. 100°C ?
(a) At 250°C – Gaseous state since it is beyond its boiling point.
(b) At 100°C – It is at the transition state as the water is at its boiling point. Hence it would be present in both liquid and gaseous states.
For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
It is due to the latent heat as the heat supplied to increase the temperature of the substance is used up to transform the state of matter of the substance; hence, the temperature stays constant.
Suggest a method to liquify atmospheric gases.
It can be achieved by either increasing the pressure or decreasing the temperature, which ultimately leads to the reduction of spaces between molecules.
Exercise - 1.4
Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
It is because the temperature is high and less humid on a hot dry day, enabling better evaporation. High levels of this evaporation provide better cooling effects.
How does the water kept in an earthen pot (matka) become cool during summer?
An earthen pot is porous in nature. These tiny pores facilitate the penetration of water and hence their evaporation from the pot surface. The process of evaporation requires energy which is contributed by water in the pot as a result of which water turns cooler.
Why does our palm feel cold when we put on some acetone or petrol, or perfume on it?
Acetone, petrol, and perfume are volatile substances that evaporate when they come in contact with air. Evaporation is facilitated as it uses energy from the palm, hence leaving a cooling effect on our palms.
Why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer rather than a cup?
A saucer has a larger surface area than a cup, promoting quicker evaporation. Hence, the tea or milk in a saucer cools down faster.
What type of clothes should we wear in summer?
In summer, it is preferred to wear light-coloured cotton clothes because light colour reflects heat and cotton materials have pores that absorb sweat, facilitating evaporation, and hence causing a cooling effect on the skin.
Exercise 1.5
Convert the following temperature to Celsius scale.
(a) 293K (b) 470K
0°C=273K
(a) 293K= (293 – 273)°C = 20°C
(b) 470K= (470 – 273)°C = 197°C
Convert the following temperatures to the Kelvin scale.
(a) 25°C (b) 373°C
0°C = 273K
(a) 25°C = (25+273)K = 298K
(b) 373°C = (373+273)K = 646K
Give reason for the following observations:
(a) Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid.
(b) We can get the smell of perfume while sitting several metres away.
(a) At room temperature, naphthalene balls undergo sublimation wherein they directly get converted from a solid to a gaseous state without having to undergo the intermediate state, i.e., the liquid state.
(b) Molecules of air move at a higher speed and have large intermolecular spaces. Perfumes comprise substances that are volatile, which scatter quickly in air, becoming less concentrated over a distance. Hence, we are able to smell perfume sitting several metres away.
Arrange the following in increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles – water, sugar, oxygen.
Oxygen (gas) < water (liquid) < sugar (solid)
What is the physical state of water at –
(a) 25°C (b) 0°C (c) 100°C?
(a) At 25°C, the water will be in liquid form (normal room temperature)
(b) At 0°C, the water is at its freezing point, hence both solid and liquid phases are observed.
(c) At 100°C, the water is at its boiling point, hence both liquid and gaseous states of water (water vapour) are observed.
Give two reasons to justify –
(a) Water at room temperature is a liquid.
(b) An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
(a) Water persists as a liquid at room temperature since its melting point is lower than room temperature and its boiling point (100o C) is higher.
Similarly,
(i). A fixed volume is occupied by a fixed mass of water.
(ii). At room temperature, water does not have a fixed shape and flows to fit the container’s shape.
As a result, water is a liquid at room temperature.
(b) Because its melting and boiling points are above room temperature, an iron almirah is a solid at room temperature. In the same way,
(i) An iron almirah is rigid and has a predetermined shape.
(ii) Metals have a relatively high density.
As a result, at room temperature, iron almirah is a solid.
Why is ice at 273K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
At 273 K, ice will absorb heat energy or latent heat from the medium to overcome fusion and transform into water. As a result, ice has a greater cooling impact than water at the same temperature since water does not absorb the excess heat from the medium.
What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam?
Steam produces severe burns. It is because it is an exothermic reaction that releases a high amount of heat which it had consumed during vaporization.
Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing a change in its state.
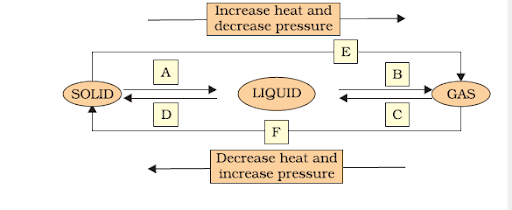
Interconversion of three states of matter: Using temperature or pressure, any state of matter can be turned into another.
(A) Solid to Liquid → Melting (or) fusion (or) liquefaction
(B) Liquid to Gas → Evaporation (or) vaporization
(C) Gas to liquid → Condensation
(D) Liquid to Solid → Solidification
(E) Solid to Gas → Sublimation
(F) Gas to Solid → solidification
Frequently Asked Questions
The NCERT solution for Class 9 Chapter 1: Matter in Our Surroundings is important as it provides a structured approach to learning, ensuring that students develop a strong understanding of foundational concepts early in their academic journey. By mastering these basics, students can build confidence and readiness for tackling more difficult concepts in their further education.
Yes, the NCERT solution for Class 9 Chapter 1: Matter in Our Surroundings is quite useful for students in preparing for their exams. The solutions are simple, clear, and concise allowing students to understand them better. They can solve the practice questions and exercises that allow them to get exam-ready in no time.
You can get all the NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 from the official website of the Orchids International School. These solutions are tailored by subject matter experts and are very easy to understand.
Yes, students must practice all the questions provided in the NCERT solution for Class 9 Science Chapter 1: Matter in Our Surroundings as it will help them gain a comprehensive understanding of the concept, identify their weak areas, and strengthen their preparation.
Students can utilize the NCERT solution for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 effectively by practicing the solutions regularly. Solve the exercises and practice questions given in the solution.

