Heinrich Rudolf Hertz: The Founder of Electromagnetic Waves
By Harshitha |
Date 01-10-2024
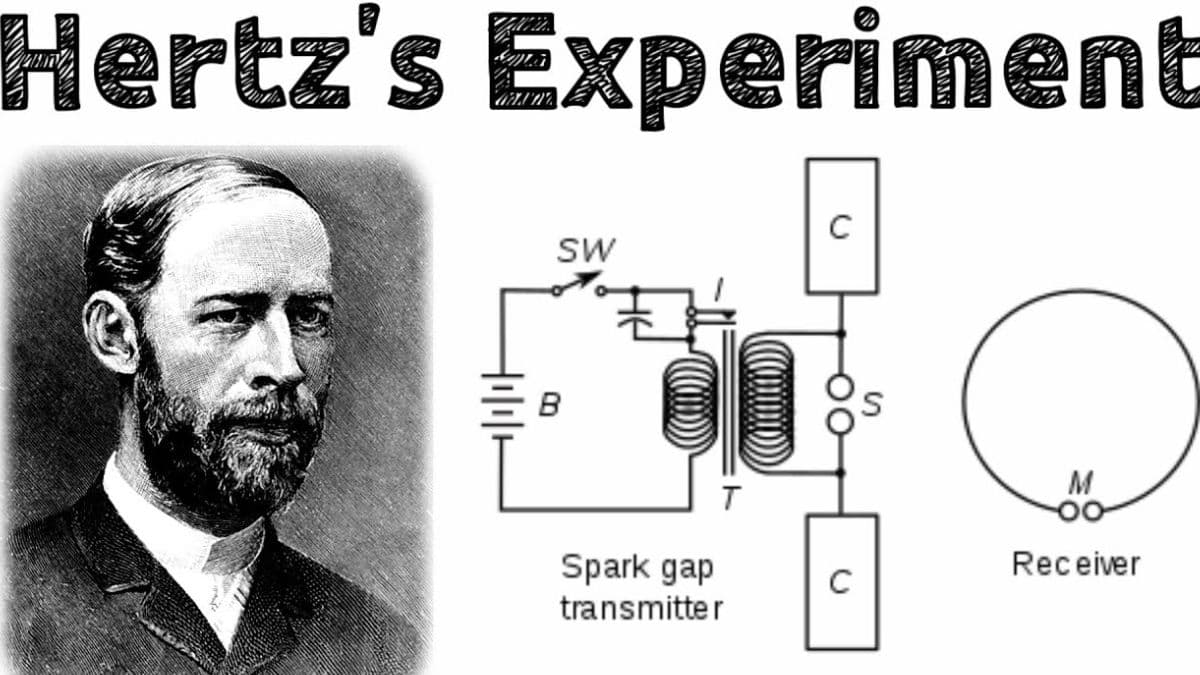
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Heinrich Rudolf Hertz
- Heinrich Hertz: A Short Biography
- Heinrich Rudolf Hertz's Contribution to Electromagnetic Wave Theory
- Inventions and Innovations of Heinrich Hertz
- The Legacy of Heinrich Rudolf Hertz
- Fun Facts About Heinrich Rudolf Hertz
- The Wider Ramifications of Hertz's Discoveries
- Conclusion
- FAQ’s
Admissions Open for
Welcome to another absolutely great virtual adventure in the world of science! Today, we are going to take a fantastic tour through the life and achievements of a brilliant scientist known as Heinrich Rudolf Hertz. You probably have never heard of his name, but everything that he found out has deeply influenced the world. So let's plunge into the exciting story of Heinrich Hertz and learn about his incredible input to science!
Introduction to Heinrich Rudolf Hertz
Heinrich Hertz was born in the 1800s and is considered one of the German researchers who did some work on electromagnetic waves. In fact, electromagnetic waves are those that fall into the category of energy of light, as well as radio waves and anything greater by far. Truly, his findings opened doors to quite a number of modern technologies-from radios to cell phones that utilize his work. But who exactly was this Heinrich Rudolf Hertz, and what was so special with his work? Well, let's find out!
Heinrich Hertz: A Short Biography
Early Life and Schooling
The biography of Heinrich Rudolf Hertz starts in Hamburg, Germany, where he was born on February 22, 1857. Since childhood, Hertz had been deeply interested in science and mathematics. His preliminary education was brilliant, and soon he managed to become an exemplary student. He had studied at the University of Munich, where many great scientists, including Wilhelm Röntgen, inspired him; later, he went on to study at the University of Berlin. In his educational career, Hertz showed an avid curiosity in understanding nature and the laws which govern it.
Early Career
After education, Hertz started his scientific work and began to solve different problems of physics. First of them was to work with electricity and magnetism, laying the foundation for his sensational discoveries. Later, he worked as an assistant in the laboratory of a famous physicist Hermann von Helmholtz, where he got great experience and learned much about work with experiments.
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz's Contribution to Electromagnetic Wave Theory
The main work of Heinrich Hertz was dedicated to electromagnetic waves. But what did he actually discover, and why is it so important? Let's see in detail.
Basic Ideas of Electromagnetic Waves
By definition, electromagnetic waves are energy waves that go through space. It includes visible light, radio, and X-rays. In fact, Hertz's experiments showed not just that light is a wave, but that those other forms of electromagnetic waves must also be waves based on the same general properties as light was. He observed that electromagnetic waves traveled at the speed of light and had similar behaviors to visible light: reflection, refraction, and interference.
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz's Experiment
One of the most famous things that Hertz ever did in his life involved an experiment with electromagnetic waves. It was near the close of 1880 that Hertz carried out experiments on the proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves. For generating those waves, he used an apparatus called a spark gap transmitter and then detected them using a loop of a wire known as a resonator. This had finally become the first time anyone was able to produce and then detect the electromagnetic waves, which proved they traveled through space just like light!
Detailed Explanation of the Spark Gap Transmitter
A spark gap transmitter has been the pivotal part of experiments through Hertz. It was composed of two metal spheres, separated by a very small gap. By activating the gap, which also develops electromagnetic waves, a spark is developed by passing a high-voltage electric current across it. Hertz, with this device, studied properties of such waves with their wavelength and frequency. The transmitter permitted Hertz to study in great detail methods that made it possible to influence and measure electromagnetic waves; this required him to make some fundamental determinations about their nature.
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz's Contribution to Electromagnetic Wave Theory
The contribution of Heinrich Rudolf Hertz towards the development of electromagnetic wave theory was monumental. Not only did he prove that such types of waves existed, but he also managed to work out that they had to follow exactly the same mathematical rules upon which light is governed. Of course, this was a giant leap forward, since it was a result of experimental approval of the theoretical work of James Clerk Maxwell on electromagnetic waves. Maxwell, according to his equations, predicted that such waves exist, and now it was confirmed by Hertz's experimentations, which was what the scientists really needed.
Validation of Maxwell's Equations
But the work he had done was, to some extent, a proof of the theory given by James Clerk Maxwell, formulated in the 1860s, which showed the interaction of electric and magnetic fields with each other in terms of wave propagation. What these experiments by Hertz carried out provided theoretical evidence to back Maxwell's theory, for it was able to prove that electromagnetic waves travel at that speed of light and do indeed have properties like wavelength and frequency. This last was already a long stride toward the actual verification, with its general theoretical aspects, of electromagnetic wave theory.
Inventions and Innovations of Heinrich Hertz
While working with his experiments with electromagnetic waves, Hertz made several other contributions to science. We try bringing more of it by highlighting some of his major inventions and innovations.
The Spark Gap Transmitter
The most significant of the inventions of Hertz was probably the spark gap transmitter. This was an electromagnetic wave generator that Hertz was using in his experiments. It simply consisted of two metal spheres, positioned a short distance apart, which provided for a high-voltage arc to jump across that distance and thereby generate the electromagnetic waves. This device was crucial for Hertz's experiments and helped pave the way for future technologies.
Resonator
In addition to the spark gap transmitter, Hertz employed as a detector another device called the resonator to detect electromagnetic waves. The resonator was a circular loop of wire tuned to the same frequency as that of the waves developed by the transmitter. These waves, upon incidence on the resonator, induce a small electric current in it, which he was able to measure. Thus, this setup enabled him to study the properties of electromagnetic waves with much clarity.
Hertzian Waves
Hertz also discovered what, today, are referred to as Hertzian waves. These are electromagnetic waves that he successfully produced and detected during his experiments. They are named in his honor and are the foundational basis for most technologies used today, including but not limited to radio, television, and wireless communication.
Impact on Wireless Communication
It was this serendipity-the discovery of Hertzian waves-that made many points clear and marked a turning point in wireless communications. By showing that electromagnetic waves can indeed be propagated through space, Hertz made possible the development of not only radio and television broadcasting systems but also virtually all forms of modern wireless communication such as Wi-Fi and cell phones.
The Legacy of Heinrich Rudolf Hertz
Modern Technology Implications
Only the work of Heinrich Rudolf Hertz eventually made its stamp on modern technologies. His research on electromagnetic waves formed a base upon which radio, television, and cellular phones would be built. No RF wireless technology exists today that wouldn't have been possible without the experiments carried out by Hertz.
Radio Technology Evolution
The work of Hertz on electromagnetic waves ushered in radio technology. Later, these findings were what the pioneers such as Guglielmo Marconi and Nikola Tesla needed to come up with the first practical radio systems. Indeed, the 1901 transatlantic radio transmission which Marconi made, for which he is considered to have pulled off a feat in the history of communication, wouldn't have materialized without the foundational elements by Hertz.
Recognition and Honors
The work of Heinrich Rudolf Hertz was noticed during his lifetime and after it, hence the naming of some scientific institutions and terms after him. Also included is the unit for frequency, the Hertz (Hz), being the measure of cycles per second in a wave, while characterizing radio waves, sound waves, and other types of oscillations.
Educational Institutions and Honors
A number of awards and institutes bear the name of Hertz to remember him. Most of the universities and research institutes have established scholarships and research programs in his name. An example of this is the Hertz Foundation, which encourages young scientists and engineers to build on pioneering research, as Hertz himself would have loved.
Fun Facts About Heinrich Rudolf Hertz
Given below are some interesting facts that relate to Heinrich Rudolf Hertz:
Young Genius: Hertz was a child prodigy in mathematics and science. In his teens, he had already attained special brilliance in them.
Short Life: His life, notwithstanding all the incredible feats that this genius contributed to the annals of science, was unfortunately rather short. At the tender age of 36, he was called to his eternal rest, though his discoveries continue to talk for him.
Name in Science: The unit of frequency was named Hertz, after him. Starting from the frequency of your computer's processor to radio waves used for broadcasting, this unit is omnipresent in everyday technology.
Love for Experimentation: Hertz was known for hands-on science. He liked experimenting and making devices to check his theories. This reflects his interest in practical investigation.
The Wider Ramifications of Hertz's Discoveries
Advances in Communications Technology
The discoveries made by Hertz relating to electromagnetic waves led to, among other things, a rapid advance in communications technology. Be it radio, television, or the latest mobile phones, the principles involved in these communication devices owe their very existence to the facts unearthed by Hertz. In fact, he succeeded in sending messages over a distance wirelessly for the first time in history.
Hertz's experiments had a great influence on physics in that they confirmed the wave-like nature of electromagnetic radiation and supported the theoretical work of Maxwell. These were some of the validating factors that went on to contribute to the quantum theory and description of light and radiation, influencing generations of physicists thereafter.
Conclusion
Heinrich Hertz was a physicist who pioneered electromagnetic waves, thus revolutionizing the way we had known the world. What Heinrich Rudolf Hertz contributed to the scientific world and what he managed to unfold through an experiment with regard to electromagnetic waves will prove that his discovery shaped the modern technological era, from radios to cell phones.
Remember, science is replete with amazing discoveries, inspired by such figures as Heinrich Rudolf Hertz. By learning about the lives of great scientists and everything they contributed, we surely learn to appreciate the technologies and innovations filling our lives with so much ease and excitement.
If you have any questions or would like to read more about other interesting scientists and their discoveries, please feel free to let me know. Until next time, keep exploring and discovering all the wonders of science.
FAQ’s
1. What was Heinrich Hertz electromagnetic wave theory?
The end of the 19th century saw Heinrich Hertz perform a revolution in the thought on electromagnetic wave theory, by proving that indeed electromagnetic waves existed and producing experiments showing how these waves might both be generated and detected. It confirmed James Clerk Maxwell's predictions and formed the foundations for modern wireless communication.
2. Who founded electromagnetic waves?
The credit of experimental discovery of electromagnetic waves was given to Heinrich Hertz. He carried out experiments in the 1880s, which were the first direct evidence for Maxwell's theories on electromagnetism.
3. Who is the father of electromagnetic radiation?
James Clerk Maxwell has been termed as the father of electromagnetic radiation because he explained the behavior of electric and magnetic fields and how these interact with matter by the set of equations known as Maxwell's equations.
4. Who is the father of frequency?
And when it comes to the "father of frequency" title it's really given to Heinrich Hertz because he proved himself to be the first person, who had demonstrated experiments of practical application of frequency in electromagnetic waves by forming the principles of wireless communication based on his experiments.
Explore the fascinating journey of Heinrich Rudolf Hertz and his groundbreaking contributions to electromagnetic waves! If you found this article insightful, share it with others to inspire curiosity about the wonders of science!
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities
- CBSE Schools in Bangalore
- CBSE Schools in Mumbai
- CBSE Schools in Pune
- CBSE Schools in Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools in Chennai
- CBSE Schools in Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools in Kolkata
- CBSE Schools in Indore
- CBSE Schools in Sonipat
- CBSE Schools in Delhi
- CBSE Schools in Rohtak
- CBSE Schools in Bhopal
- CBSE Schools in Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools in Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools in Jaipur
- CBSE Schools in Jodhpur
- CBSE Schools in Nagpur
- CBSE Schools in Ahmednagar
- CBSE School In Tumkur

Call Us to know more about Orchids
Swipe Up



.jpg&w=1920&q=80)












