Electromagnetic Induction: Sparks For the Modern Age
By Harshitha |
Date 01-10-2024
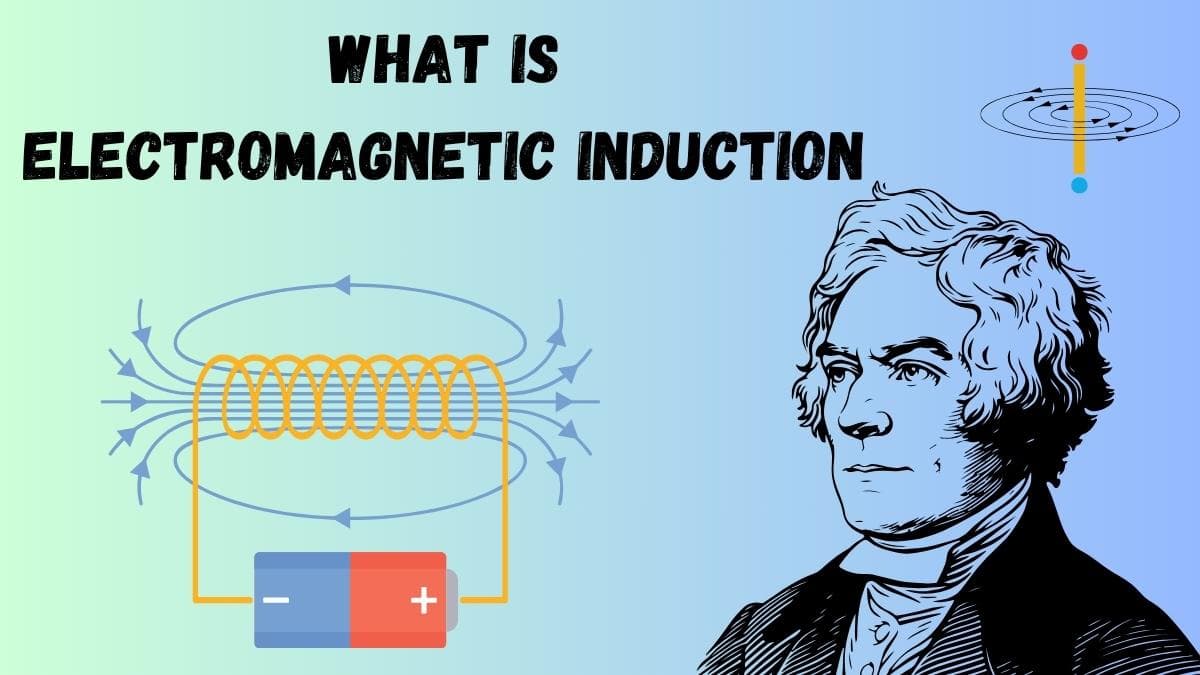
Table of Contents
- Radioactive Pollution - What is it?
- Radioactive Elements and Their Role
- Radioactive Pollution and Its Impact
- What is Radioactivity?
- Definition of Radioactive
- How Electromagnetic Induction Relates to Radioactivity
- Practical Uses of Electromagnetic Induction
- The Importance of Safe Handling of Radioactive Elements
- Learning from Past Experiences in Order to Protect the Future
- Search for Alternatives: Renewable Energy and Electromagnetic Induction
- The Future of Electromagnetic Induction and Energy Production
- Conclusion: The Power of Knowledge
- FAQs :
Admissions Open for
Ever thought how electrical energy is generated, or how gadgets work? Well, the answer lies in an interesting process termed electromagnetic induction. This is one scientific concept behind running everything in our daily lives, from our homes to smartphones. But before going deeply into the details of electromagnetic induction, let's explore a topic related to it-radioactive pollution-and learn about its impact upon our world.
Radioactive Pollution - What is it?
Before we begin with electromagnetic induction, a little understanding of radioactivity is in order. But first, just what is radioactivity? Radioactivity is the natural process by which some radioactive elements emit energy in the form of radiation. These elements, such as uranium and plutonium, have atoms that are unstable. To achieve a more stable state they release energy; we call this energy radiation. This radiation comes in the form of particles and electromagnetic waves.
Radioactive pollution is brought about by the accidental or willful leakage of these radioactive elements or materials into the environment. It may result from a nuclear accident, leak, or fall of radioactive materials in transport, radiation treatment application using nuclear devices and atomic energy's hazardous byproducts, unhygienically disposed nuclear waste, or radioactivity from an explosion of an atomic bomb.
Radioactive Elements and Their Role
Having touched upon radioactive pollution, let us now move ahead to understand the underlying radioactive elements. Radioactive elements naturally occur in the Earth as well as can be prepared in laboratories. What differs from all other substances is that they are unstable. This instability leads them to disintegrate at predetermined half-lives while giving off radiation.
For example, uranium is a naturally occurring radioactive metal that is largely used in many nuclear power plants. The decay of atoms inside uranium releases energy, which can be harnessed as electricity. However, it highly contributes to radioactive pollution if not well handled.
Radioactive Pollution and Its Impact
Radioactive pollution is hazardous because these elements emit harmful radiation to living organisms. When living organisms-human beings, animals, etc.-are exposed to huge doses of radiation, the cells and DNA are damaged. The consequence can be serious diseases like cancer and other congenital disabilities. Radioactive pollution contaminates water, soil, and air, which in turn can be very disastrous for plants, animals, and humans alike.
One of the most known accidents in radioactive pollution is the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, which happened in Ukraine in 1986. A very huge amount of radioactive material was released into the environment from the explosion that happened at the plant. The area surrounding the plant is still contaminated, and it will take many years before it is safe for people to live there.
What is Radioactivity?
First, it is important to understand what radioactivity is in order for better understanding. Radioactivity describes the procedure through which energy is released by radioactive elements while they decay. The process usually occurs in some elements naturally, like uranium, radon, and thorium. These atoms have got too much energy hence making them unstable. To achieve stability, they release the extra energy in the form of radiations.
The type of radiation emitted may be one or more of the following: alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays. Each of them presents different characteristics and resulting hazards. Alpha particles are much less dangerous and stopped even by a sheet of paper, whereas gamma rays are of grave concern and highly penetrating for virtually anything, including human tissue.
Definition of Radioactive
What then is meant by radioactive? The term "radioactive" borrows from a word known as "radioactivity," or, for simple mankind, the ability of some elements to emit radiation while decaying. When an object is termed radioactive, it is because of the elements it contains, which are considered radioactive and release radiations. Such radiations pose a danger, especially
when the levels are high or the exposure is for a long duration. Knowing the radioactive meaning helps us in understanding the precautions that we take, which might generally be obstructive, not to cause radioactivity in our environment and protect living beings from harmful radiation.
How Electromagnetic Induction Relates to Radioactivity
Now that we have learned something about radioactive pollution and the very basics of radioactivity, let's go ahead and connect it to electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic induction is a phenomenon discovered by Michael Faraday in the 19th century. It is an electric current developed owing to the variation of the magnetic field around a conductor, such as a wire.
This process is critical in producing electricity at the power station level. The amazing thing here is that this heat, which produces the steam to run the turbines connected to generators, is from radioactive elements in some nuclear generating stations. These generators work on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
Whereas electromagnetic induction as a principle provides an excellent means toward the generation of electricity, radioactive elements involved in this process should be kept well under close management for avoiding radioactive pollution. This in turn would require proper handling and disposal of the nuclear waste to prevent radiation from leaking into the environment .
Practical Uses of Electromagnetic Induction
Electromagnetic induction is everywhere. The principle refers, among other things, to the generation of electricity in your home using useful small gadgets.
Electric Generators: The most widespread use of electromagnetic induction is found in electric generators. They work through the conversion of mechanical energy-the turning of a turbine, for example-into electrical energy. It is the principle of action behind coal, hydroelectric, and nuclear power plants. In the latter, the heat from decaying radioactive elements makes steam that can turn a turbine coupled to a generator.
Transformers: Another application is in transformers, which are useful in changing the voltage of electricity; this electricity travels from power plants to your home. Without transformers, it would just not be possible to transfer electrical energy over a long distance efficiently. The working of transformers basically depends on electromagnetic induction, transferring energy between circuits through a changing magnetic field.
Induction Cooktops: Induction cookers in your kitchen exploit electromagnetic induction. Instead of heating the burner, these cookers heat your pots and pans directly by magnetic fields. This cooks food more quickly and efficiently.
Wireless Charging: Exactly through the same principle, one can recharge, say, smartphones wirelessly. A so-called charging pad generates a magnetic field inducing a voltage in the receiver coil of the device to be charged. The resulting current drives the charging process without any cables.
The Importance of Safe Handling of Radioactive Elements
The advantages of electromagnetic induction are evident, but when radioactive elements become involved in the generation of electricity, safety comes first. Radioactive pollution is acute because when radioactive materials are released to the environment, their containment becomes really hard to achieve.
Nuclear Waste Disposal: Among the largest challenges of radioactivity element utilization is the concept of nuclear waste disposal. The waste produced continues to be harmful for as long as several thousand years and has to be stored in safety, isolated facilities to avoid any risk of leakage causing radioactive pollution.
Nuclear accidents: Nuclear accidents have always been tragedies; an example is the Chernobyl disaster. Besides extremely long-term health effects, a very large amount of radio-active substances gets released into the environment, which in turn causes damage to the environment. This again stresses the fact that radioactive elements are to be treated with ample care and safety measures.
Radiation protection: Radiation protection involves the use of protective gear by individuals who work in an environment completely filled with radioactive elements. Safety precautions at work will also be a must for them to minimize radiation exposure that will protect their health due to radioactive pollution.
Learning from Past Experiences in Order to Protect the Future
Understanding the radioactive meaning and the dangers of radioactive pollution is crucial for the future. Indeed, as long as nuclear power remains in our source of energy, past mistakes should be taken as lessons to make sure the radioactive elements are treated with extreme caution.
Also, further research into less hazardous nuclear technologies and improved radioactive-waste storage facilities will reduce the risk of radioactive pollution. In the future, more awareness among people about radioactivity and its consequences on environmental health will make them more responsible toward the use of nuclear energy.
Search for Alternatives: Renewable Energy and Electromagnetic Induction
While nuclear power and its utilization of radioactive elements have their efficiencies, there are other forms of generating electricity through electromagnetic induction that do not involve the risks associated with radioactive pollution. These include renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power.
Wind Power: Wind turbines generate power from the aerodynamic energy produced by the wind. The wind makes the turbines rotate. The rotating motion is conveyed to a generator comprising magnets and coils. Due to the fact that the turbine blades are rotating, they constantly change the magnetic field in the generator. This change in magnetic field leads to electromagnetic induction of electricity. It is clean and there's no form of harmful radiations.
Solar Electricity Generation: Electric energy is directly produced from sunlight by solar panels; indirectly, it is used for heating water to produce steam and drive turbines. Again, electromagnetic induction is involved as the turbines drive generators to create electricity.
Hydroelectric Power: Hydroelectric dams are one way in which the flow of water has been utilized to turn turbines connected to generators. This again uses electromagnetic induction, similar to the flow generated by wind and solar input, to produce electricity without radioactive pollution.
The Future of Electromagnetic Induction and Energy Production
This of course automatically means that electromagnetic induction will remain very important in the near and coming future. Nevertheless, we are likely to proceed with cleaner renewable sources of energy which do not involve radioactive elements. This would reduce radioactive pollution and give room for a safer environment for future generations.
All these will further cultivate innovation in electromagnetic induction, coming up with new technologies that will improve the lives of people-from efficient energy production to advanced medical equipment. These possibilities are limitless, and electromagnetic induction as science will further keep driving technology forward.
Conclusion: The Power of Knowledge
Understanding electromagnetic induction, radioactive pollution, and the relationship with radioactive elements can foster an appreciation of the very complex world of energy production. Radioactive elements have their place in the generation of electricity; it is just important to handle them responsibly, so as not to create radioactive pollution.
Generally speaking, learning about what radioactivity is and about its effects will help us gain more knowledge in deciding how humanity can gain better alternatives for producing energy without harm to people or the Earth. Be it a new way of using electromagnetic induction or a solution to radioactive pollution in general, knowledge is the most powerful weapon.
These topics will allow the curious child to know how physics is close to our life and has affected it. By asking more questions, finding answers, and working on these questions, we can create a future that integrates technology and nature in perfect harmony using clean and safe energy for all.
FAQs :
What is electromagnetic induction in modern technology?
Electromagnetic Induction is a current produced because of voltage production (electromotive force) due to a changing magnetic field. This either happens when a conductor is placed in a moving magnetic field (when using an AC power source) or when a conductor is constantly moving in a stationary magnetic field.
What is electromagnetic induction used for today?
The principle of electromagnetic induction is used in electronic components such as inductors and transformers. Electromagnetic induction is the basis of all types of electric generators and motors used to generate electricity from motion and motion from electricity.
How is electromagnetism used in modern technology?
If we didn't understand electromagnetism, cell phones wouldn't exist. Those are just a few of the many technological applications of electromagnetism. Others include televisions, doorbells, speakers, videotapes, and any type of magnet. Electromagnetism is everywhere.
We hope you liked the above article. Please do not forget to share this blog with your friends and community members to spread awareness of "Electromagnetic Induction."
Related Blogs
Faraday's Thumb Rule: Get to know about Faraday's Thumb Rule and other fun facts through our blog.
Charles Augustin de Coulomb: Get to know about Charles Augustin de Coulomb and his Law through our latest blog!
George Simon Ohm: Get to know about George Simon Ohm through our latest article!
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities
- CBSE Schools in Bangalore
- CBSE Schools in Mumbai
- CBSE Schools in Pune
- CBSE Schools in Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools in Chennai
- CBSE Schools in Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools in Kolkata
- CBSE Schools in Indore
- CBSE Schools in Sonipat
- CBSE Schools in Delhi
- CBSE Schools in Rohtak
- CBSE Schools in Bhopal
- CBSE Schools in Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools in Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools in Jaipur
- CBSE Schools in Jodhpur
- CBSE Schools in Nagpur
- CBSE Schools in Ahmednagar
- CBSE School In Tumkur

Call Us to know more about Orchids
Swipe Up

.jpg&w=1920&q=80)














