Have you ever wondered, if humans and apes shared ancestors, why aren’t chimpanzees or apes evolving into Humans?
The answer is simple: Humans did not evolve from Chimpanzees or any species of Apes. We share entirely different evolutionary paths. We have shared a common ancestor that lived approximately 10 million years ago.In this article, we’ll explore the major 7 stages of human evolution, highlighting key species and the milestones that shaped our evolution.
What is Evolution?
Evolution is the process through which living organisms evolve from simple unicellular organisms. In simple words, evolution means the slow process of change in the organism from a simple structure to a more complex one. According to the English scientist Charles Darwin, evolution depends on the mechanism of natural selection that results in the increased reproductive capacities of organisms best suited for their living conditions. Darwin’s theory was that every organism evolves due to many slight changes that happen over time. This article will discuss stages of Human evolution during pre-human times and human prehistory. During prehistory, no evidence of writing was found. However, much important information on prehistory is obtained through studies of the fossil record.
History of Human Evolution
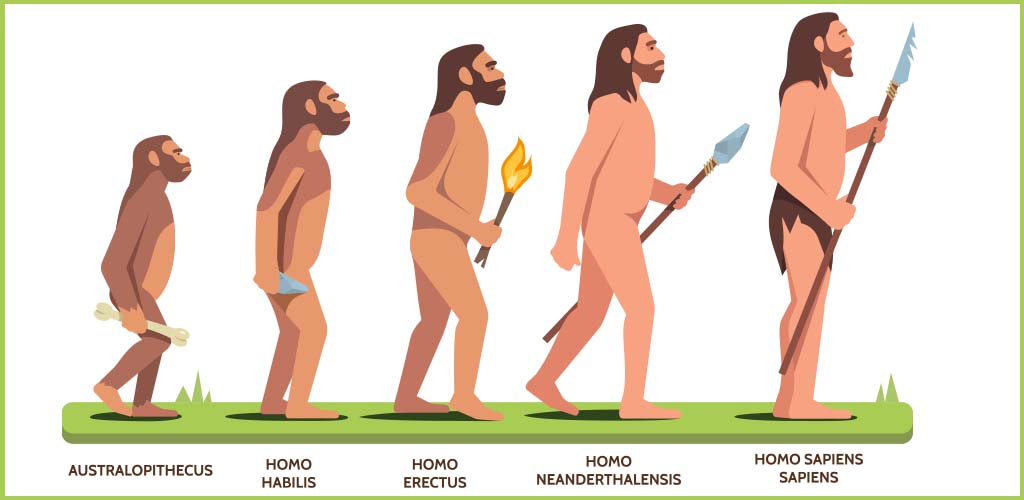
The evolution of man began approximately millions of years ago when the first known man walked this earth. Present-day humans developed through many stages of human evolution, from early hominins or primates that are now extinct.
The genus of the human being today is called Homo, and the man today is called Homo Sapiens. The development of multicellular organisms from simple unicellular life forms is a lengthy evolutionary process- from the primates of humans who walked on all four limbs to the modern-day man who walks on two hind limbs.
7 Stages of Human Evolution
These are the 7 stages of Human Evolution explained below:
Dryopithecus
[Dry·o·pi·the·cus]
The genus Dryopithecus or the oak wood apes are considered the common ancestors of man and apes. They lived in China, Europe, Africa, and India. When Dryopithecus was alive, its tropical lowlands were densely forested. Thus, the members could have predominantly been herbivores.
Ramapithecus
[Ra·ma·pi·the·cus]
The first remains of Ramapithecus were discovered in the Shivalik range of Punjab. Later some remains were found in Africa and Saudi Arabia also. They believed in living in open grasslands. Two pieces of evidence confirm their Hominid status:
– Thickened tooth enamel, shorter canines, and robust jaws.
– Extrapolations of upright posture and usage of hands for food and defence.
Australopithecus
[Aus·tra·lo·pith·e·cus]
The fossil of Australopithecus was first discovered in South Africa in 1924. They were approximately 4 feet tall and weighed 60-80 pounds. They started living on the ground, using stone tools as weapons and erecting their body posture while walking.
Homo Habilis
[Ho·mo ha·bi·lis]
Homo Habilis – The name of this genus signifies ‘handyman’ in Latin, representing them as the first makers of tools. They have larger braincases and smaller faces as compared to Australopithecus. They were upstanding. Homo Habilis was adjusted to living on trees.
Homo Erectus
[Homo] [erec·tus]
The first fossil of this genus was found in Java in 1891. These were named Pithecanthropus Erectus and were considered the missing link between man and apes.
Another discovery of Homo Erectus was made in China. The discovery of the Peking man- a specimen that had large cranial capacities. Homo Erectus is believed to have lived in communities. They used tools comprising quartz, bones, and wood. There is evidence of collective hunting and the use of fire. This genus is believed to dwell in caves.
Homo Sapiens Neanderthalensis
[Ho·mo] [sa·pi·ens] [Ne·an·der·thal·ian]
The Homo Erectus evolved into Homo Sapiens. This species of hominids could hunt big animals such as Mammoths. During evolution, the two subspecies of Homo Sapiens were identified- Homo Sapien Neanderthal & Homo Sapiens Sapiens. The cranial capacity (used to measure the size of the brain) of Neanderthal grew from 1200 to 1600 cc. There were some small hand axes that had been discovered.
Homo Sapiens Sapiens
[Ho·mo] [sa·pi·ens]
The remains of Homo Sapiens Sapiens were first discovered in Europe and were named Cro-Magnon. In this genus, the jaws are quite reduced, the modern man’s chin appears, and the skull is rounded. Their cranial capacity was about 1350 cc. They gathered food through hunting. Art first appeared during this time.
Stages of Human Evolution by Charles Darwin
According to Darwin’s famous book The Origin of Species – evolution has come through a series of natural selection. This theory can be emphasized in the following points:
- Natural Selection– is the mechanism of evolution of a species wherein characteristics which assist character organisms in living on and reproducing are surpassed directly to their offspring.
- Struggle for Existence– Organisms multiply in geometric ratio—an increase withinside the number of species results in conflict for existence.
- Survival of the Fittest-According to Darwin, withinside the conflict for existence, the fittest one will survive.
- Variation– According to Darwin, beneficial versions seem in each generation and are inherited from one generation to another.
This is how the stages of human evolution came to light. The genetic variations in early ancestor populations favoured new abilities to adapt to environmental change and altered the human way of life.These 7 stages of human evolution showcase an incredible journey, from early primates to modern Homo sapiens.
Frequently Asked Questions
1) What are the Different Types of Evolution?
Answer-Here's how the types and stages of human evolution unfolded :
- Parallel Evolution: In this type of Evolution, two different species evolve independently of each other. The species are unrelated; this evolution doesn’t need to occur in the same habitat or niche.
- Divergent Evolution: In this, two closely related species evolve from a common ancestor or parent but become different from each other.
- Convergent Evolution: In this Evolution, two unrelated species share common characteristics due to the same habitat. For example, whales and sharks live in water, but their origins differ.
2) Are Chimpanzees Direct Ancestors of Humans?
Answer- Humans and Chimpanzees share common ancestors, but they are not related directly.
3) What are the 7 stages of human evolution?
Answer-
- Dryopithecus. These are deemed to be the ancestors of both man and apes. ...
- Ramapithecus. ...
- Australopithecus. ...
- Homo Erectus. ...
- Homo Sapiens Neanderthalensis. ...
- Homo Sapiens Sapiens.
Other Related Sections
NCERT Solutions | Sample Papers | CBSE SYLLABUS| Calculators | Converters | Stories For Kids | Poems for kids | Practice Worksheets | Formulas I Parent Resources



Speak Your Mind
Save my name, email and website in this browser for next time I comment