Air Around Us for Class 6
Air Around Us
Air is present all around us, but it is difficult for the unaided eye to see. It encompasses us, in the ground & high into the cosmos. Even though air is invisible, it is essential for the existence of life. Everything that is alive needs air, and without air, we humans, animals, and even plants will cease to exist. Even more exotic are things like of natural phenomena like weather, clouds, or even machines.
Wind is the motion of air - Air is always moving in our surroundings. It also influences the heat of their environment. Well, the air that we breathe is essential for balance and life on Earth.
Layers of Atmosphere
The atmosphere is a sheath of gases that surrounds the Earth. It's held in place by gravity and is a vital ingredient in the continuation of life on this planet. The atmosphere extends from the surface of the Earth to as high as 10,000 kilometers.
There are layers in the atmosphere:
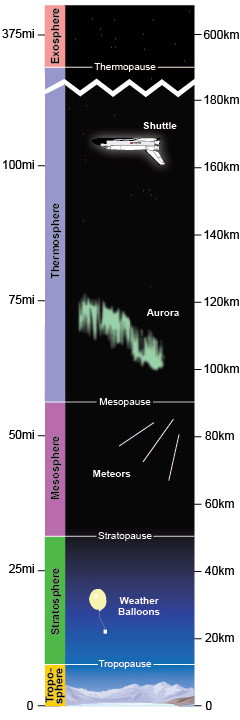
Troposphere
-
Height: Up to ~12 km
-
Features:
-
Closest to Earth’s surface
-
Weather happens here (clouds, rain, wind)
-
Temperature decreases with height
-
Contains about 75% of the atmosphere's mass
-
Stratosphere
-
Height: ~12 km to ~50 km
-
Features:
-
Contains the ozonosphere (ozone-rich region)
-
The ozone layer is found here, between 15 to 35 km
-
Absorbs harmful UV rays from the sun
-
Temperature increases with height due to absorption of sunlight by ozone
-
Jet planes often fly in this layer to avoid weather
-
Mesosphere
-
Height: ~50 km to ~85 km
-
Features:
-
The coldest layer of the atmosphere
-
Meteors burn up here
-
Thermosphere
-
Height: ~85 km to ~600 km
-
Features:
-
Temperature increases with height (can exceed 2000°C)
-
Contains the ionosphere (helps in radio communication)
-
Auroras (Northern/Southern Lights) occur here
-
Space stations orbit in this layer
-
Exosphere
-
Height: ~600 km and beyond
-
Features:
-
Outermost layer, merging into outer space
-
Extremely thin air, mostly hydrogen and helium
-
Satellites orbit here
-
Source: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
Composition of Air
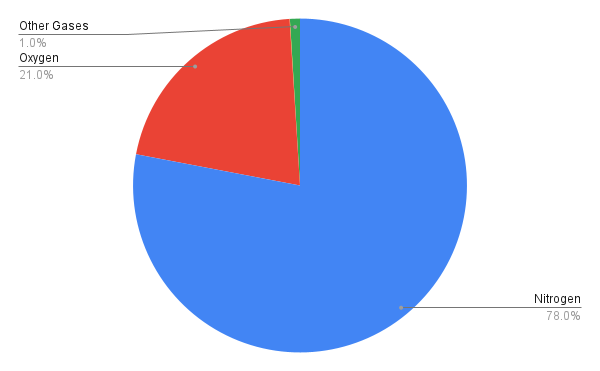
Air composition is a reference to the ratio of gasses that are inside the air near you. The air around us is mainly made up of the following gases:
-
Nitrogen (78%): The largest amount of gas present in the air is nitrogen. It plays a crucial role in the air — it moderates the other gases & hinders their acute reactions — not that it’s of much direct help to the majority of life forms.
-
Oxygen (21%): Oxygen is essential for respiration in living organisms. It is also used by animals & plants to extract energy from food during a process called cellular respiration.
-
Carbon Dioxide (0.03%): In a few tenths of a percent, carbon dioxide is a small part of the air we breathe, but it exists as a part of photosynthesis. It also helps Earth’s temperature stay steady by trapping heat in the atmosphere (the greenhouse effect).
-
Argon (0.93%): An inert gas; it does not react with other substances & has no direct integral use for life.
-
Other Gases (0.01%): These include trace amounts of neon, helium, methane, & others.
Composition of Air
Importance of Air
The air is very important for the survival of living beings. Each of the components has its own essential & important function:
-
Oxygen: Without it, humans & animals would be unable to breathe, cellular respiration would not occur, and energy could not be created.
-
Nitrogen: Nitrogen is inert, and it works as a way to dilute surrounding oxygen in the air so it doesn’t ignite spontaneously. It is also involved in the nitrogen cycle & helps in plant growth.
-
Carbon Dioxide: The next important gas is carbon dioxide, the way that plants feed themselves, through the process of photosynthesis. It is also the organism that transforms light power into important energy in the form of chemical power types, and it is the start of most food cycles. Plants absorb carbon dioxide, which they use when they photosynthesize, and give off oxygen, which animals & humans then breathe in.
-
Water Vapor: Although the amount of water vapor is less in the atmosphere, it plays an integral role in the development of clouds & precipitation. It also helps regulate Earth’s temperature and sustain the water cycle.
The composition of these gases in the air is necessary for life on Earth. Disruption of this balance can lead to trouble, as in the case of climate change, the consequence of excess carbon dioxide & other heat trapping gases.
Uses of Air
Air has many uses in our lives. Without air, Earth would be a very different place. Let us have a look on few usages of air around us:
-
Breathing: One of the most common purposes of air is respiration. It was animals, including humans, that needed oxygen in the air to breathe & live. Lungs absorb oxygen, which then goes into the cells, where it is used to extract energy from food.
-
Photosynthesis: Absorption and creation of O2 by plants: While taking carbon dioxide from the surrounding air, a process occurs called photosynthesis whereby plants produce food & O2 is released as a by-product. This cycle is essential for life on Earth.
-
Fire: Fire needs air to carry on the process of combustion. All fires need oxygen to burn. Without it, the flames would perish.
-
Transportation: Hot air balloons, planes & even rockets depend on air for their function.
-
Weather and Climate: This is important to us, so we need to protect it so that air is an essential element in forming clouds and rain. It does the atmosphere the temperature, it does the balance of hot & cold.
Air is the life-blood of Earth, and its uses are at the heart of the sophisticated, useful science and industry. Air is even composed of various elements essential to all living things, the atmosphere creates the proper conditions for life.
Fun Facts
- Air is composed of 78% nitrogen; this does not aid in directly sustaining life.
- Oxygen is only 21% of the air, but we could not live without it.
- Plants receive the carbon dioxide that we exhale & give us the oxygen we inhale.
- The vapor in the air around us is essential for clouds & rain.
Things you have learned!
- Air is all around us, even though we cannot see it. All living things need air to stay alive.
- The atmosphere has five layers – each layer has a special job, like making weather or protecting us from harmful rays.
- Air is made of different gases – mostly nitrogen and oxygen, and a little carbon dioxide, argon, and water vapor.
- Each gas in the air is important – oxygen helps us breathe, carbon dioxide helps plants make food, and water vapor forms clouds and rain.
- Air helps us in many ways – we need it to breathe, for fire to burn, for flying planes, and for making weather.

